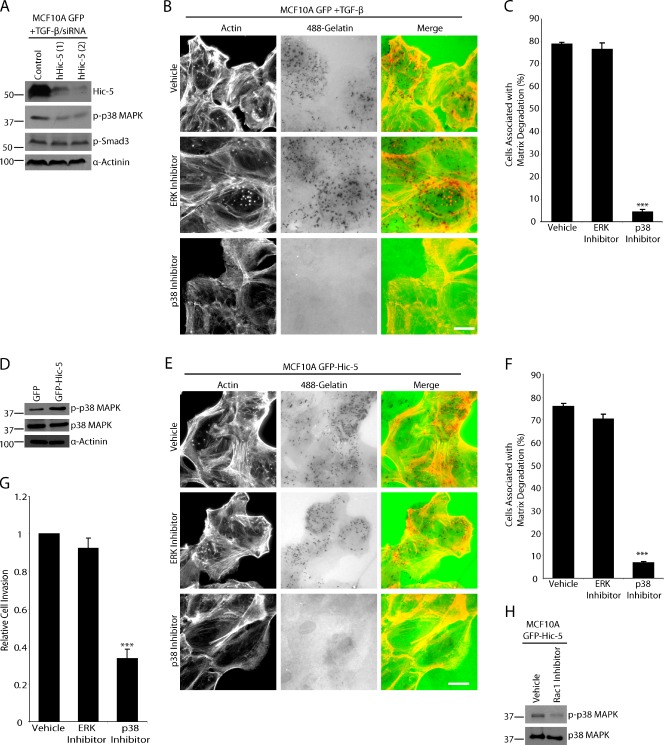
Figure 8.
Matrix degradation by TGF-β–treated MCF10A cells or unstimulated GFP–Hic-5 MCF10A cells is dependent on p38 MAPK activity but not ERK. (A) TGF-β–treated MCF10A GFP cells were treated with control and hHic-5 siRNAs (hHic-5). Endogenous hHic-5 depletion reduces the level of p38 MAPK phosphorylation but not SMAD3 phosphorylation. (B) TGF-β–treated MCF10A GFP cells were plated on fluorescent 488–gelatin in the presence of vehicle, MEK/ERK inhibitor U0126, or p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580. The p38 MAPK inhibitor blocked degradation, whereas the ERK inhibitor had no effect. Bar, 20 µm. (C) Quantitation of TGF-β–treated cells degrading matrix in the presence of inhibitors. (D) Western blot analysis showing that unstimulated GFP–Hic-5 cells have elevated levels of p38 MAPK phosphorylation. (E) GFP–Hic-5 cells plated on fluorescent gelatin in the presence of p38 MAPK and ERK inhibitors. P38 MAPK inhibition blocked matrix degradation. Bar, 20 µm. (F) Quantitation of GFP–Hic-5–expressing cells degrading matrix in the presence of inhibitors. (G) Invasion through Matrigel is reduced in GFP–Hic-5–expressing MCF10A cells by the p38 MAPK inhibitor, but not by ERK inhibition. ***, P < 0.0005. (H) Treatment of GFP–Hic-5 cells with Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 reduces the level of phospho-p38 MAPK. Molecular mass standards are indicated next to the gel blots in kilodaltons. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.