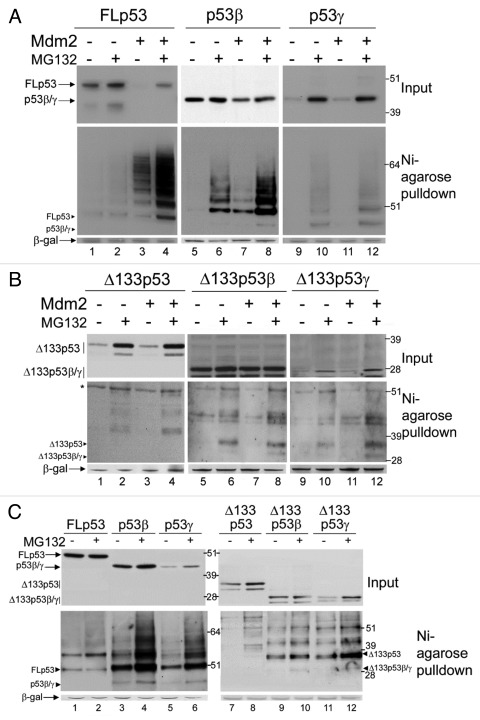
Figure 4. Ubiquitination and degradation of p53 isoforms. (A) 1μg FLp53 (lanes 1–4), p53β (lanes 5–8) or p53γ (lanes 9–12) was expressed in H1299 cells in the absence (lanes 1–2, 5–6 and 9–10) or presence (lanes 3–4, 7–8 and 11–12) of 2μg co-expressed Mdm2. Three hours prior to harvesting cells were treated or left untreated, as indicated, with MG132. In all cases 2μg His6-tagged-ubiquitin was co-transfected and DNA concentrations were maintained with empty pcDNA3 control vector. A Ni-agarose purification of His6-tagged ubiquitinated species is shown in the lower panel and corresponding whole cell extract in the upper panel. The molecular weight of each unmodified isoform is indicated with a labeled arrowhead for all ubiquitin-purification assays. (B) As in (A) but Δ133p53, Δ133p53β or Δ133p53γ were expressed instead of FLp53, p53β or p53γ, respectively. A background band detected by DO-12 is indicated with an asterisk *. (C) p53 isoforms are ubiquitinated in Mdm2-negative cells. 1μg FLp53 (lanes1–2), p53β (lanes 3–4), p53γ (lanes 5–6), Δ133p53 (lanes 7–8), Δ133p53β (lanes 9–10) or Δ133p53γ (lanes 11–12) was co-expressed with 2μg His6-tagged-ubiquitin in DKO cells. Cells were treated as indicated with MG132 and His6-tagged ubiquitinated proteins were purified with Ni-agarose. Whole cell extracts are shown in the upper panel and Ni-agarose purification in the lower panel. β-gal was used as a loading and transfection-efficiency control throughout.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.