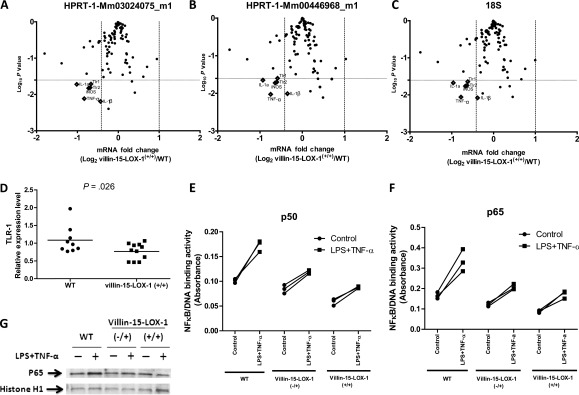
Figure 3.
Effects of 15-lipoxygenase-1 (15-LOX-1) transgenic expression on nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling in colonic epithelial cells. See Supplementary Methods (available online). A–C) Effects of 15-LOX-1 transgenic expression on NF-κB signaling pathways. Homozygous villin-15-LOX-1-A transgenic mice (villin-15-LOX-1+/+) and control (wild-type [WT]) mice were treated with azoxymethane (AOM) and killed 20 weeks later as described in Supplementary Methods (available online). Gene expression was measured in isolated normal colonic crypt epithelial cells using TaqMan low-density array assays. Data were normalized to levels obtained with either HPRT-1 mRNA probe A (Mm00446968_m1), HPRT-1 mRNA probe B (Mm03024075_m1), or 18S ribosomal RNA. C). Volcano plots are shown that relate the fold changes in NF-κB signaling pathway–related gene expression in nonmalignant colonic mucosa between these two groups of mice. Diamonds indicate genes with more than 25% reduced expression levels (P values were determined by two-sided Student's t test P values < .025). D) Effects of 15-LOX-1 transgenic expression on Toll-like receptor-1 (TLR-1) expression in colonic epithelial cells. TLR-1 mRNA expression was measured using quantitative reverse transcription real-time polymerase chain reaction in normal colonic crypt epithelial cells of individual villin-15-LOX-1-A transgenic and control WT mice treated with AOM as described for panels (A–C). Values are the means of triplicate measurements for each mouse. P values were determined by two-sided Student's t tests. E and F) Effects of 15-LOX-1 transgene expression on NF-κB activation. Primary colonic epithelial cells were isolated from the indicated mice and were treated with either 10 μg/mL lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and 10 ng/mL tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) or with vehicle solution as a control. NF-κB binding to its DNA consensus site was measured by TransAM ELISA assays with specific p50 (E) or p65 (F) antibodies. Values shown are the means of triplicate measurements for each mouse. G) Effects of 15-LOX-1 transgenic expression on p65 protein levels in the nucleus. Nuclear protein fractions were extracted from isolated colonic epithelial cells treated with either LPS and TNF-α or control vehicle solution as described for panels (E) and (F). Proteins were immunoblotted and probed with p65 and histone H1 antibodies. Representative blots for the three indicated types of mice are shown.