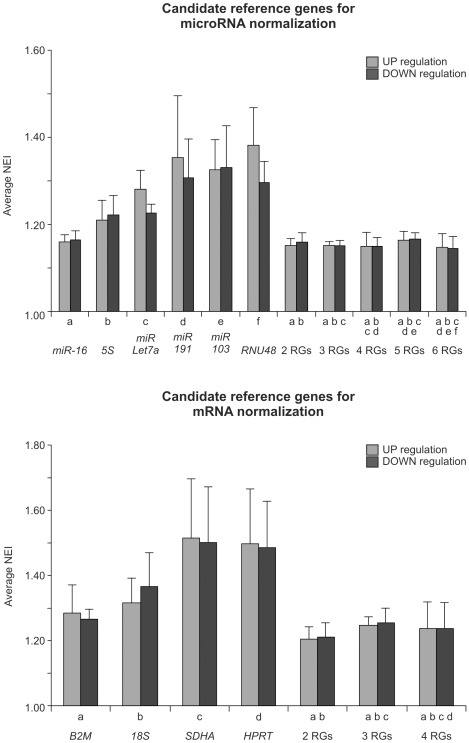
Figure 4. Study of the normalization efficiency of candidate reference genes.
The average normalization efficiency index (NEI) of the four treatments for each microRNA or mRNA normalization method and their corresponding standard deviation are shown in up- and down-regulation situations. For each treatment with a specific hepatotoxin, we defined the NEI value as the minimum fold up- or down-regulation of the simulated expression of a hypothetical gene needed to observe a significant difference (t test, p = 0.05, n = 5) using different methods of normalization. The liver expression value of one or combination of reference genes (RGs) was used to normalize the expression of the hypothetical gene. The liver expression of RGs were assessed 24 h after rats were intraperitoneally administered with: acetaminophen (AA, 1.2 g/kg body weight) or its vehicle (1% carboxymethyl cellulose, 10 ml/kg body weight); carbon tetrachloride (CT, 1 ml/kg body weight) or its vehicle (corn oil, 4.4 ml/kg body weight), D-galactosamine (GA, 0.9 g/kg body weight) or its vehicle (saline solution, 6 ml/kg body weight); thioacetamide (TA, 150 mg/kg body weight) or its vehicle (saline solution, 6 ml/kg body weight).