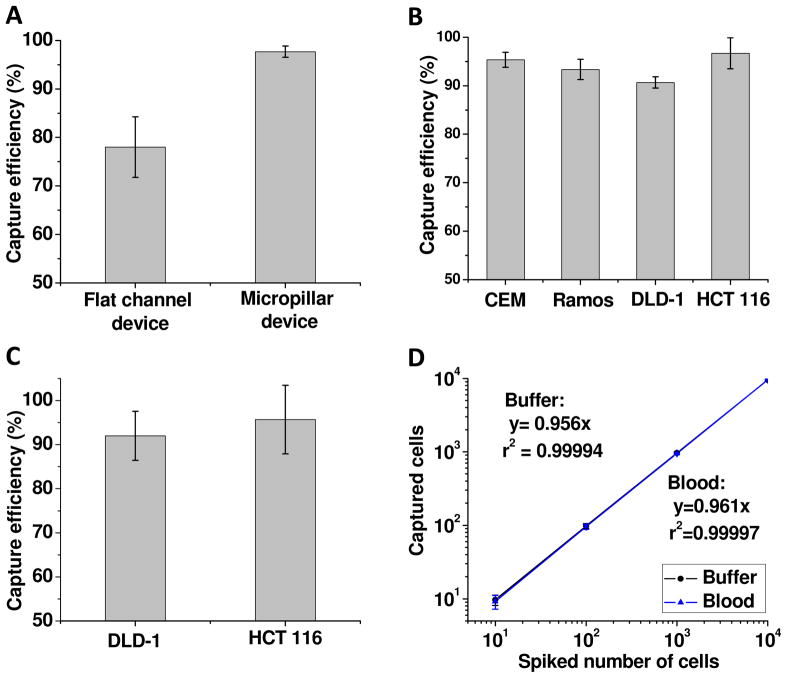
Figure 4.
(A) Comparison of the capture efficiency between a flat channel device reported previously and the micropillar device in this work. (B) Capture efficiencies of 4 types of cancer cells in the microfluidic device with micropillars. A different aptamer with specific binding with cells of interest was used for each type of cancer cells. (C) Capture efficiencies of DLD-1 cells and HCT 116 cells in whole blood. (D) Regression analysis of the number of the cells captured by the microfluidic device versus the number of the cells spiked into 1 mL of samples. Both axes are in the logarithm scale. HCT 116 cells at different concentrations were spiked either into the capturing buffer with Ramos cells as the control or into whole blood. Two calibration curves overlap with each other, reflecting no significant difference between buffer and blood samples. The error bars represent one standard deviation of 6 repeats for 10-cell samples and 3 repeats for other cell numbers.