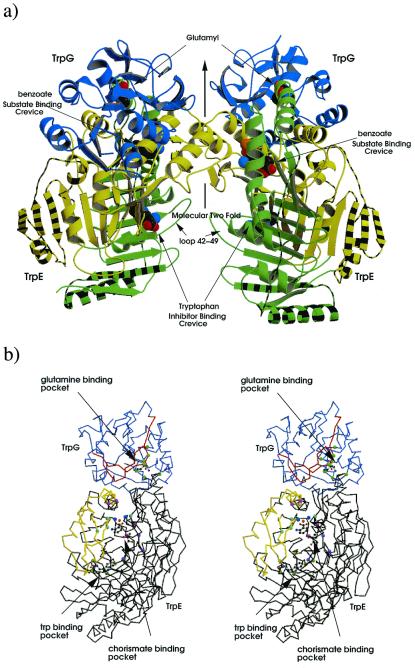
Figure 2.
Structure of the AS of S. marcescens. (a) Ribbon diagram of the AS oligomer, TrpG subunits shown in blue, TrpE subdomain I shown in green subdomain II in yellow. Striped regions correspond to additional structure in S. marcescens compared with that of S. solfataricus. Glutamyl, benzoate, pyruvate, and tryptophan are shown as cpk models. (b) Stereo diagram of the heterodimer; TrpG shown in lilac, TrpE in black; regions of TrpG that move on addition of tryptophan relative the C-crystal are shown in red, whereas those of TrpE are in yellow; residues important to the CA-binding pocket (G328, T329, H398, G485) are shown as light blue balls, residues involved in pyruvate interactions (Y449, R469, G483) are in purple, residues involved in magnesium coordination (E358,361, E495, E498) are colored light purple, magnesium ion in orange, water molecules in dark blue, Trp-binding residues (S40, P291, M293, V453, Y455) are light green, and residues involved in glutamine binding (P57, G58, G60, C85, L86, Q89, S135, S136) are in green. Benzoate, pyruvate, magnesium, and glutamyl are shown as ball-and-stick figures. Produced by bobscript and raster 3d (39–42).