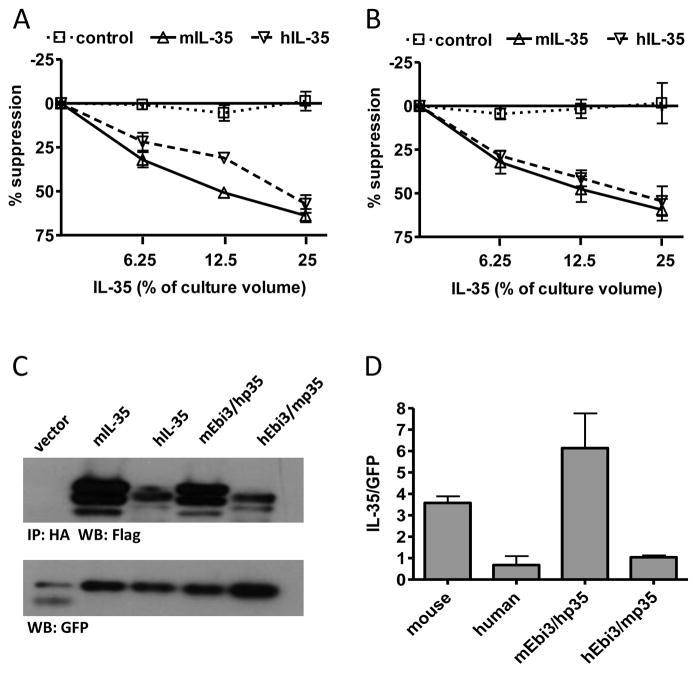
Fig. 1. IL-35 receptor interaction sites and heterodimer interface is conserved from mouse to human.
(A) CD4+ CD45RBhi CD25− T cells from C56Bl/6 mice were FACS purified and activated with anti-CD3/CD28 beads in the presence and absence of mIL-35, hIL-35 or control supernatants. Counts per minute of activated T cells alone were 30,000–50,000. (B) CD4+CD25− T cells from human cord blood were FACs purified and activated with anti-CD3/CD28 beads and 10 IU/ml IL-2 in the presence and absence of mIL-35, hIL-35 or control supernatants. Counts per minute of activated T cells alone were 50,000–100,000. Data represents mean ± SEM of 3 experiments done in duplicate. (C) 293Ts were transfected with indicated combination of mouse and human FLAG-Ebi3 and p35-HA subunits. Lysate samples were immunoprecipitated using an anti-HA antibody and immunoblotted with anti-FLAG to assess the degree of subunit pairing. Multiple bands for IL-35 are a result of multiple intracellular glycosylation species. Lysates were immunoblotted for GFP as a loading control. (D) Western blots were quantified and plotted normalized to GFP. Data represent the mean ± SEM of 4 independent experiments.