Figure 2.
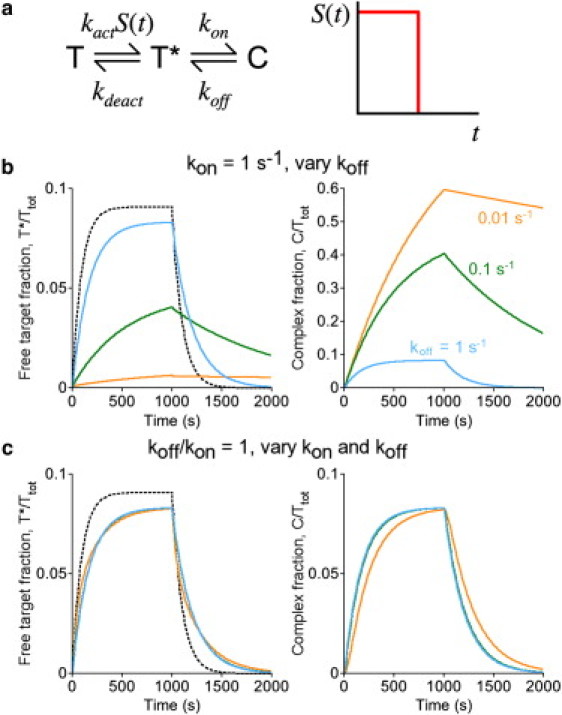
Perturbation of active target level and kinetics: intramolecular biosensors, or intermolecular biosensors expressed in stoichiometric excess. (a) Kinetic scheme for an intramolecular biosensor, following the nomenclature established in Fig. 1a; the scheme holds equally for an intermolecular biosensor expressed in excess ([B] ≈ constant). In the hypothetical scenario, stimulation (S = 1) is pulsed for a period of 1000 s. (b) The fractions of the total biosensor pool in the free, active target (T∗, left) and complexed (C, right) states are plotted as a function of time. The affinity of the molecular recognition element was adjusted by progressively decreasing the dissociation rate constant koff, as indicated: koff = 1 s−1, 0.1 s−1, or 0.01 s−1. (Dashed curve) Active target kinetics in the absence of complex formation (koff = ∞). Other parameter values were fixed at kon = 1 s−1, kact = 0.001 s−1, and kdeact = 0.01 s−1. (c) Same as panel b, except that the ratio of koff/kon was fixed at 1, with koff = kon = 1 s−1, 0.1 s−1, or 0.01 s−1.
