Figure 6.
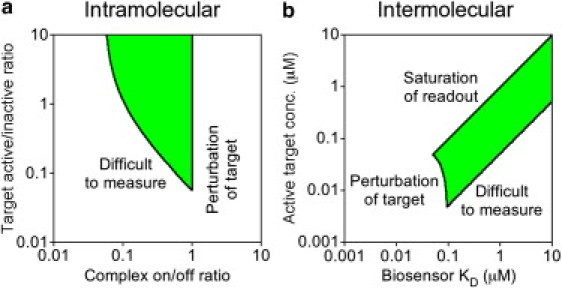
Design space for engineering suitable biosensors. In each case, a desirable region of feasibility is defined by the shaded area. (a) The design space for an intramolecular biosensor is defined by the affinity of complex formation and the extent of target activation. To the left of the desired region, 5% or less of the biosensor molecules are in complex, resulting in a readout that is difficult to measure. To the right of the desired region, 50% or more of the modified target is bound, resulting in significant perturbation of the observed kinetics. (b) The design space for an intermolecular biosensor is defined by the biosensor binding affinity and the concentration of the active target. A moderate biosensor expression level of 0.1 μM is assumed. In addition to the criteria outlined under panel a, saturation of complex formation becomes significant when the active target concentration exceeds both the concentration and binding KD of the biosensor.
