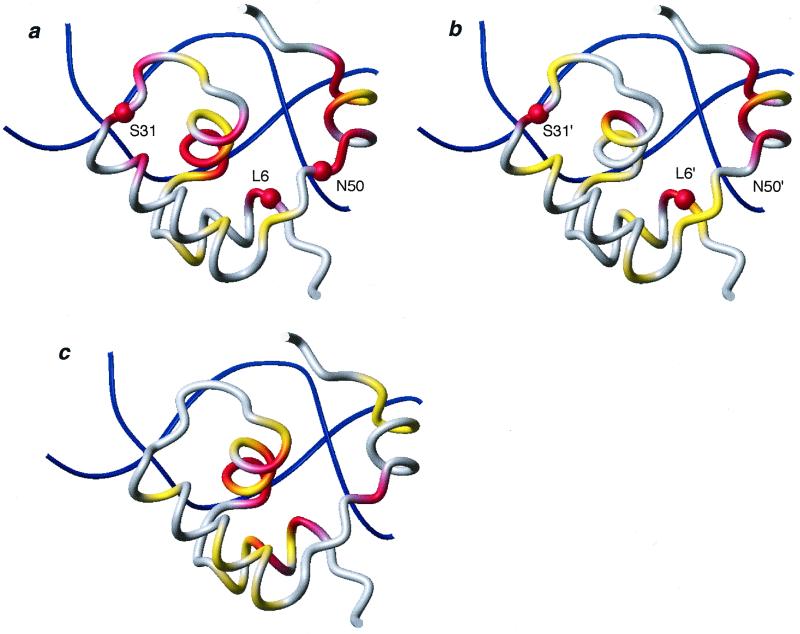
Figure 5.
Chemical shift variations of dimer HP62-V52C induced upon binding to the wild-type DNA operator. The chemical shift mapping is projected on the three-dimensional structure of the HP62-SymL(−1) complex (4). The two sites are depicted independently and have been rotated for easier comparison: (a) left site, (b) right site. (c) The chemical shift difference between bound left and right site is summarized. The color code used is as follows: |Δδav| < 0.3 ppm, gray; 0.3 ppm < |Δδav| < 0.6 ppm, yellow; |Δδav| > 0.6 ppm, red. Δδav is a weighted average of the 15N and 1HN chemical shifts (31): Δδav = 0.5[Δδ(1HN)2 + (0.2 Δδ(15N))2]1/2. Backbone amides that are involved in protein–DNA hydrogen bonding and were shown to be protected in hydrogen exchange experiments are indicated with spheres. The molecular models were drawn with MOLMOL (32).