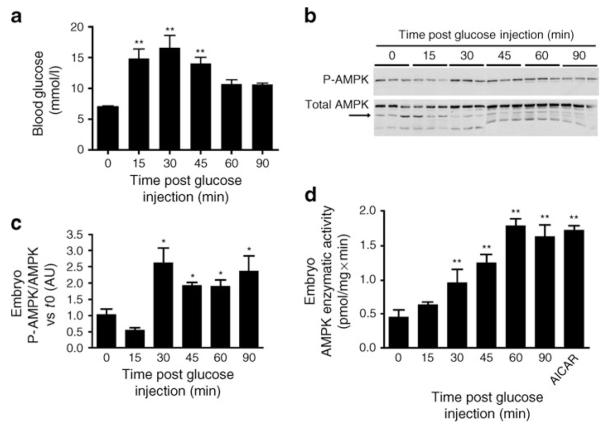
Fig. 1.
a Maternal blood glucose levels before and up to 90 min after induction of transient hyperglycaemia on E7.5 of pregnancy by s.c. glucose administration. b Immunoblot of PO4-AMPK and total AMPK from whole embryos before and up to 90 min after induction of maternal hyperglycaemia. c Quantitation of scanned bands of PO4 (P)-AMPK/total AMPK from (b). Band intensity is expressed as arbitrary units (AU) relative to time 0 (t0). d AMPK enzyme activity (pmol/mg protein × min) in embryos before or up to 90 min following induction of maternal hyperglycaemia. AMPK activity 90 min after administration of AICAR (50 mg/kg) served as a positive control. Because assay of PO4-AMPK/AMPK by immunoblot is more sensitive than assay of AMPK enzyme activity, immunoblot of PO4-AMPK/AMPK was used to measure the stimulation of AMPK activity in subsequent experiments. All panels: *p<0.05 vs t0; **p<0.01 vs t0. n = pooled embryos from three pregnancies per time point, except in (d), where six pregnancies per time point were used, and embryos from two pregnancies were pooled for triplicate reactions per time point