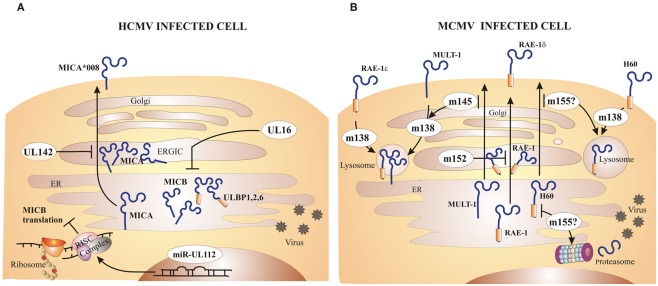
Figure 2.
Major CMV inhibitors of NKG2D ligands. Both HCMV and MCMV encode immunoevasins that inhibit expression of NKG2D ligands on the surface of infected cells. (A) The HCMV protein UL16 inhibits MICB, ULBP1, ULBP2, and ULBP6 expression by retaining them inside the cell. UL142 prevents MICA expression via retention in the cis-Golgi compartment. Certain alleles of MICA, such as MICA*008, are resistant to inhibition by HCMV due to truncation of the cytoplasmic domain. HCMV microRNA (miR)–UL112 forms RISC complex that binds to the MICB transcript and represses its translation. (B) MCMV encodes four immunoevasins that redundantly downmodulate all mouse NKG2D ligands. The m152 product retains RAE-1 family of proteins in ER/cis-Golgi compartment. Not all RAE-1 proteins are equally susceptible to inhibition by MCMV, namely RAE-1δ is more resistant than other RAE-1 proteins. The m145 product interferes with MULT-1 expression by making it more susceptible to the inhibition by the other immunoevasin, m138. The m155 product redirects H60 for lysosomal and/or proteasomal degradation. Surface RAE-1ε, MULT-1, and H60 are additionally downmodulated by m138 which interferes with their recycling.