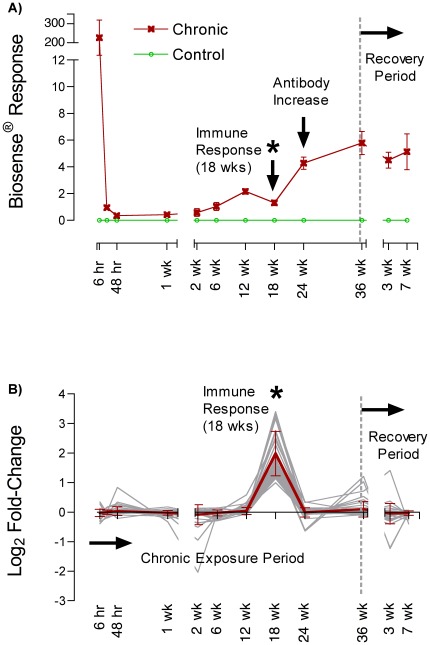
Figure 1. A) Response of Biosense® (Bergen, Norway) competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) in serum of exposed and time-matched control zebrafish (Danio rerio) at all sampling time points.
Detection by competitive ELISA indicates the presence of DA and/or DA-specific antibodies in serum. B) One K-means cluster for a set of significantly differentially expressed genes (1.5 fold; p<0.05) quantified in whole brains from exposed and control zebrafish. The y-axis represents the log2 fold-change for genes in this cluster at all sampling time points (x-axis). The K-means algorithm forces all differentially expressed genes into clusters or groups with other genes that behave most similarly over all time points. Once clusters have been formed, further analysis of the known functions of the genes within each cluster can be used to identify potentially impacted biological processes. Functional annotation clustering using DAVID (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) of the genes shown here identified Immune Function as the major functional group (enrichment score: 1.98). Up regulation of immune related genes at 18-weeks (demarked by *) indicates a significant immune response, after which antibody levels appear to rise in the blood (Figure 1A).