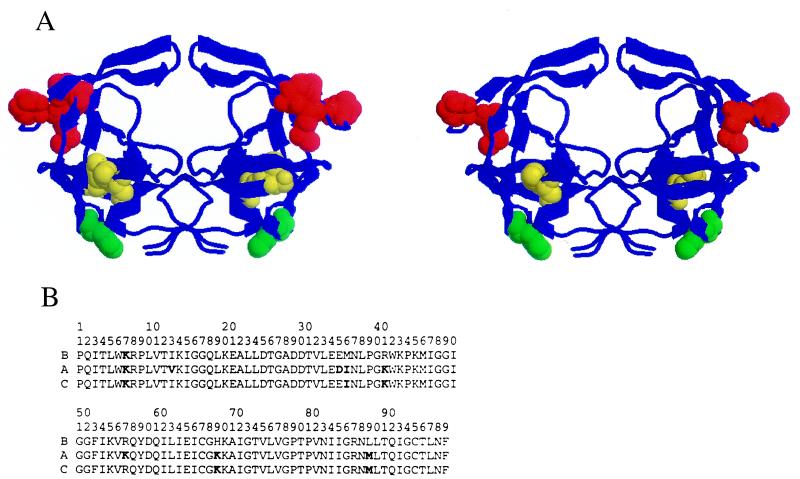
Figure 1.
(A) Structure of the HIV-1 protease showing the location of amino acid polymorphisms in the A subtype (I13V/E35D/M36I/R41K/R57K/H69K/L89M) (Left). (Right) Shown is the location of a subset of mutations (M36I/R41K/H69K/L89M) found in some C subtype and recombinant HIV-1 isolates. In the hinge of the flap, residues 36 and 41 are affected in A and C subtypes, whereas residue 35 is mostly affected in A (red). Residue 89 in the α helix is affected in A and C whereas residue 13 in the opposite β strand is predominantly affected in A (yellow). Residue 69 in the loop connecting the two β strands is affected in both the A and C proteases (green). (B) The sequences of the proteases used in these studies.