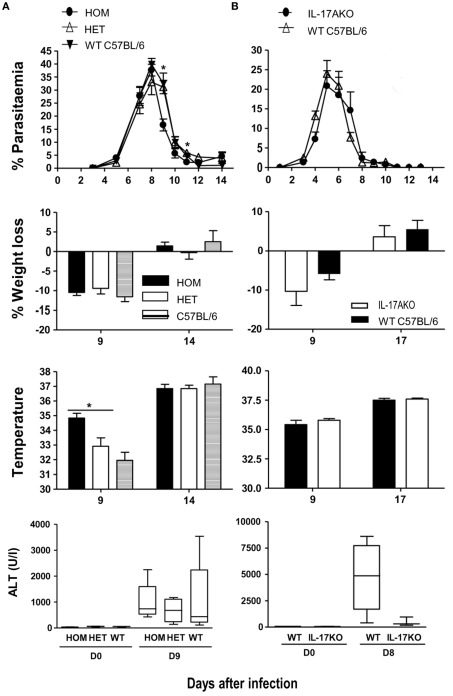
Figure 5.
Parasitemia and pathology in IL-17-fate reporter and IL-17 KO mice. (A) Il17aCre+/+R26ReYFP and conventional (B) Il17A−/− mice were infected with 105 P. chabaudi, five mice per group. The heterozygous reporter mice in (A) also act as a control for the homozygous mice as the IL-17 gene is not deleted in these mice. WT C57BL/6 mice were used as controls in (A,B). Weight loss and hypothermia (pathology) were monitored daily. Parasitemias are presented as percentage of parasitized RBC, and the error bars represents the SEMs. Tail blood was collected to measure ALT variation during the infection, using a colorimetric end-point method (adapted from Reitman and Frankel, 1957). Briefly, 20 μl of test serum was added to 100 μl of the ALT substrate and incubated for 30 min at 37°C. Hundred microliters of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine was then added and incubated a further 20 min at RT. One milliliter of 0.4 M NaOH was added to stop the reaction and the OD determined at 490 nm. Water was used as blank. OD values were then converted into the equivalent enzyme units (U/ml) using a standard curve derived from known concentrations of a pyruvate standard. The standard curve for ALT was performed using pyruvate standards. Data are means and SEM of five mice and representative of two experiments. Significant differences are shown using a Mann–Whitney U-test of five mice [*significant P-value (0.01–0.05)].