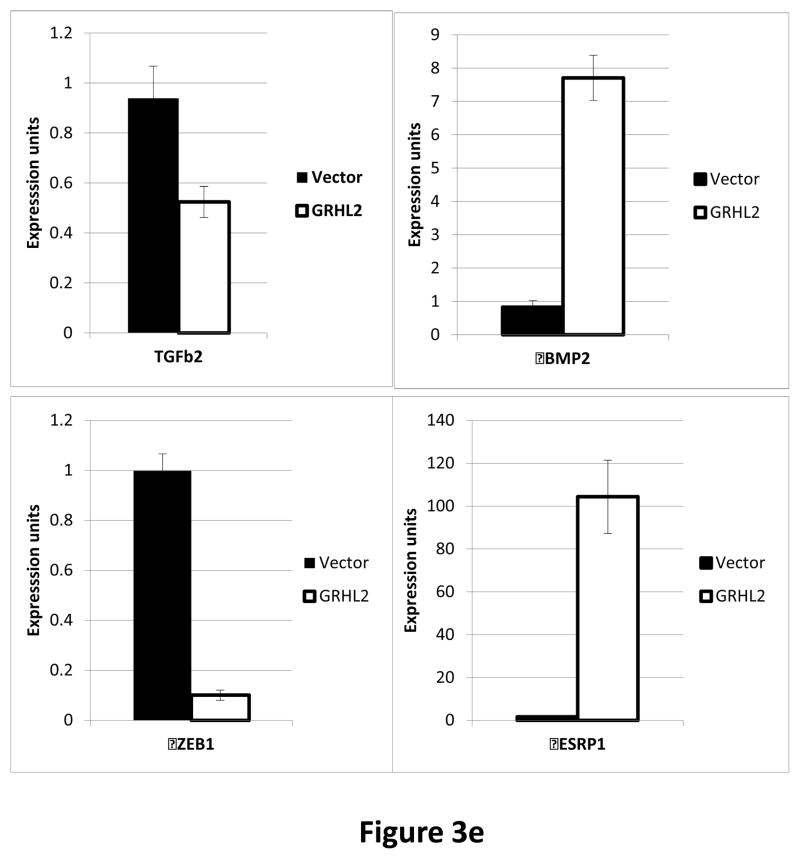
Figure 3. GRHL2 suppresses TGF-β-induced EMT.
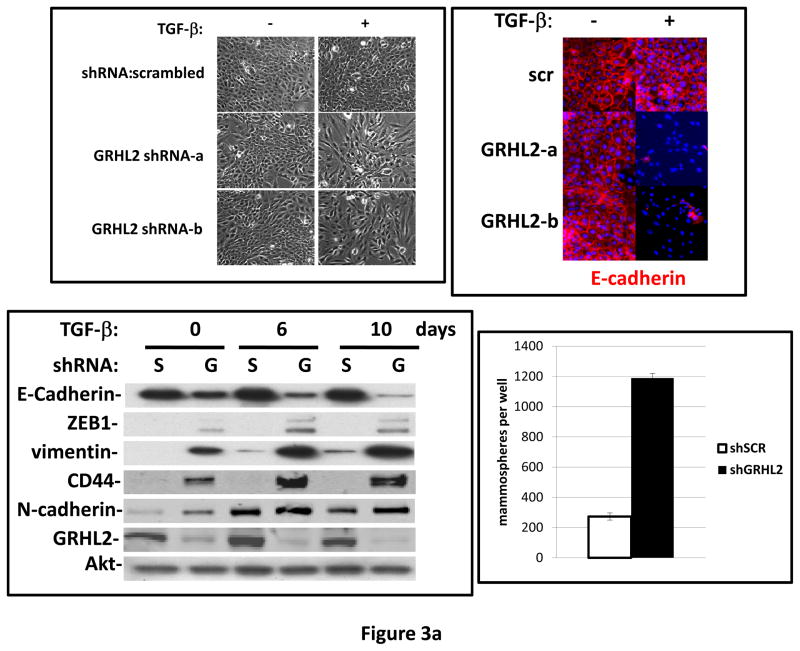
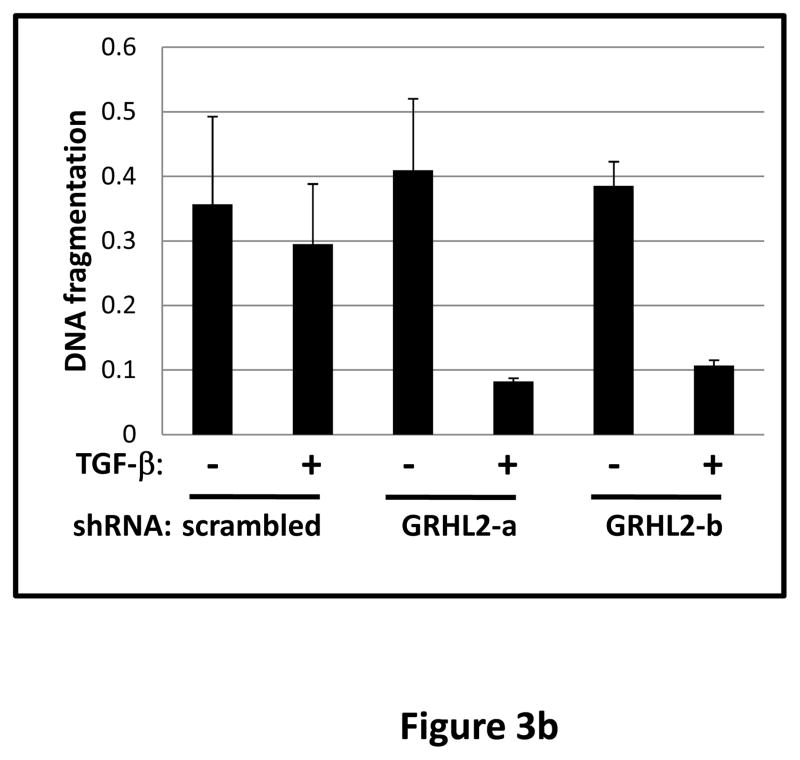
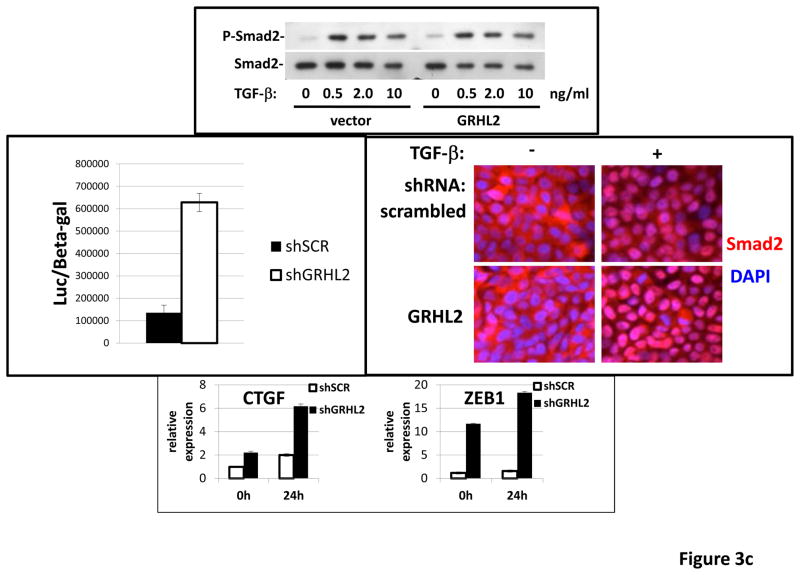
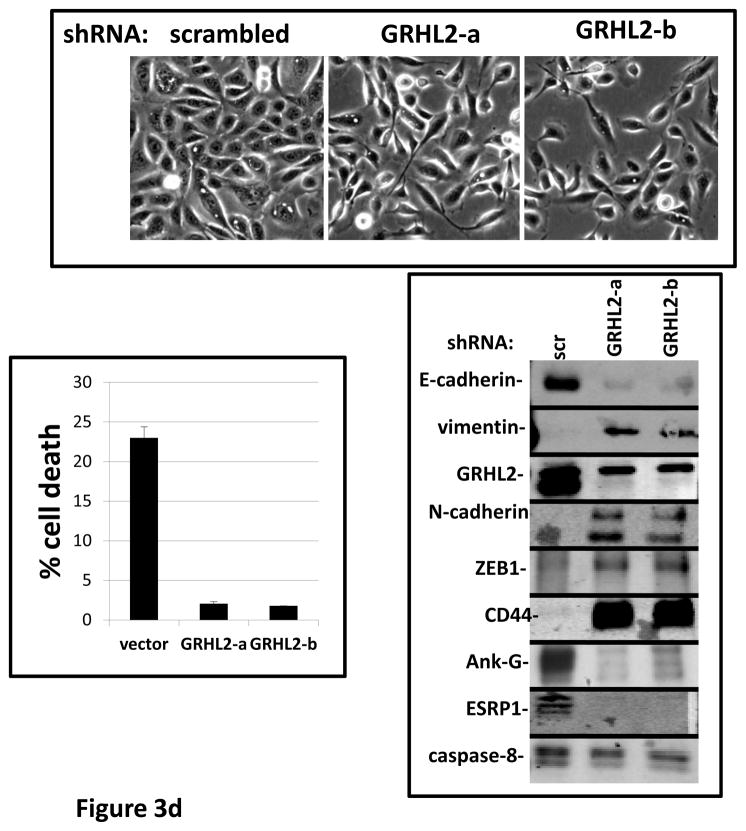
(a) GRHL2 knockdown permits HMLE cells to undergo TGF-β-induced EMT. HMLE+twist-ER cells (no 4-OHT) with two distinct GRHL2 shRNAs or a scrambled control shRNA were exposed to TGF-β for two weeks prior to analysis for cell morphology (top left), E-cadherin expression/localization (immunofluorescence, top right) or mammosphere generation (graph, lower right). Epithelial and mesenchymal markers were also analyzed at the indicated times of TGF-β treatment (western blot, lower left). (b) GRHL2 suppresses the ability of TGF-β to confer anoikis-resistance. The cell lines described above were assayed for anoikis by DNA fragmentation after two weeks incubation with or without TGF-β. (c) GRHL2 inhibits Smad-mediated transcription. (left panel): Effect of stable GRHL2 knockdown on activity of a Smad-responsive reporter construct (3TP-lux) was determined by luciferase assays of transiently transfected HMLE+twist-ER cells (no 4-OHT) expressing either scrambled or GRHL2a shRNA that were treated with TGF-β for sixteen hours prior to lysis; values are luciferase activity normalized to an internal co-transfected β-galactosidase control. (lower panel): Effect of stable GRHL2 knockdown on induction of TGF-β/Smad target genes, CTGF and ZEB1, by exogenous TGF-β, determined by qRT-PCR. (top panel): No effect of GRHL2 on phosphorylation of Smad2/3. MSP cells expressing empty vector or GRHL2 were treated with the indicated concentrations of TGF-β for 24h and analyzed for total and phospho-smad2/3. (right panel): No effect of GRHL2 on nuclear translocation of Smad2. The GRHL2 knockdown or control cells described in part a were treated with TGF-β for six hours and analyzed for Smad2 localization by immunofluorescence. (d) GRHL2 knockdown induces EMT in HMLE cells with Ras (HMLER). HMLER expressing two distinct GRHL2 shRNAs or scrambled shRNA control were imaged using phase contrast microscopy (top), immunoblotted for epithelial and mesenchymal markers (right) or assayed for anoikis (trypan blue exclusion, left panel). (e) GRHL2 up-regulates BMP2. RT-PCR was performed on RNAs from HMLE+Twist-ER cell lines with or without constitutive GRHL2 expression (induced with 4-OHT), using the indicated primer sets.