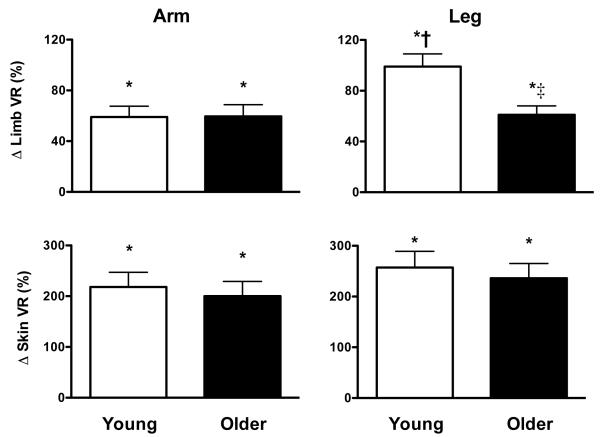
Figure 1.
Percent change (Δ) in limb and skin vascular resistance index (VR) in the arm (left panels) and leg (right panels) of young and older adults in response to limb dependency. VR index was calculated as mean arterial pressure/mean blood velocity (limb) or flux (skin). Responses are presented as the percent change from the baseline position (limb at heart level) to the dependent position (limb lowered 30 cm below heart level). Mean arterial pressure was corrected to account for the hydrostatic pressure gradient created when the limb was studied in the dependent position (mean arterial pressure in control limb at heart level + 0.766 * 30 cm). Limb VR in the arm was assessed in the brachial artery and in the leg in the popliteal artery. Skin VR in was assessed on the ventral aspect of the forearm (arm) and calf (leg). Values are mean±SE.
* P<0.05 from baseline
† P<0.05 from response in arm (same age group)
‡ P<0.05 from response in young (same limb)