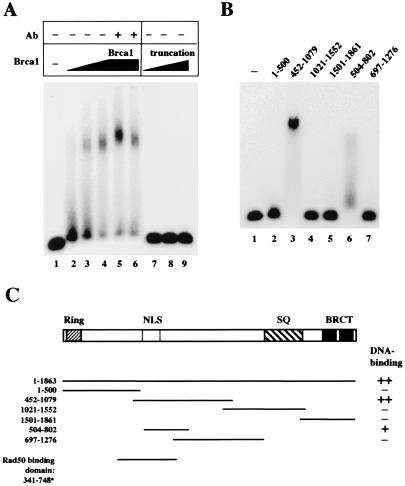
Figure 2.
Brca1 binds DNA. (A) Gel mobility shift assays were performed with full-length Brca1 (lanes 2–6) or the isolated truncated product (lanes 7–9). Approximately 10 ng of protein was added in lanes 2 and 7, 20 ng in lanes 3 and 8, and 40 ng in lanes 4–6 and lane 9. The proteins were mixed with a 32P-labeled double-stranded DNA substrate and incubated for 10 min at room temperature before electrophoresis in a 0.7% 1/2× TBE (90 mM Tris/64.6 mM boric acid/2.5 mM EDTA, pH 8.3) agarose gel. In lanes 5 and 6, 100 ng of two different antibodies directed against Brca1 was also included in the binding reaction. (B) Gel mobility shift assays were performed as in A, except with fragments of Brca1 expressed in E. coli as GST fusion proteins. Approximately 300 ng of each fragment was incubated with the DNA substrate per reaction. The amino acid endpoints of each Brca1 fragment are shown above the lanes. (C) Schematic representation of the Brca1 polypeptide and the regions covered by the various fragments expressed in E. coli. The DNA-binding activity of the fragments is indicated in the right column, with ++ denoting the highest level of binding, and + indicating partial levels of binding. The Rad50 binding domain shown for comparison at the bottom is from yeast two-hybrid data by Zhong et al. (13).