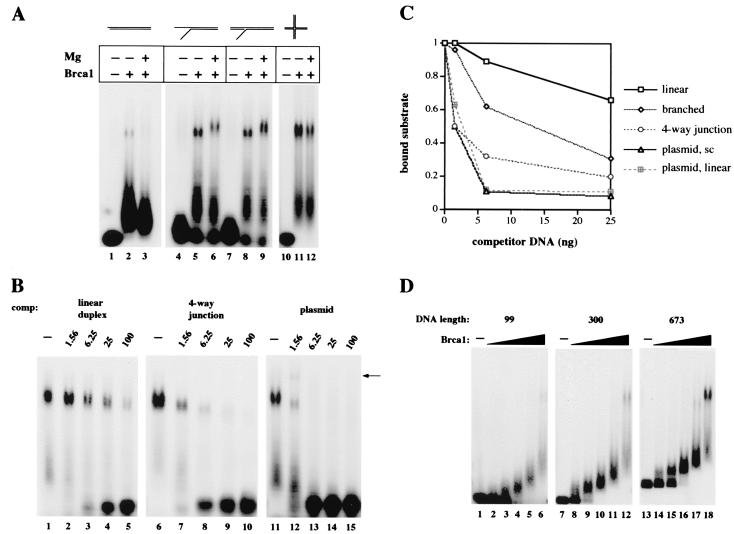
Figure 4.
Brca1 binds preferentially to branched structures and long DNAs. (A) Gel mobility shift assays were performed with 25 ng of full-length Brca1, added to reactions as indicated, on 32P-labeled linear (lanes 1–3), Y-structure (lanes 4–6), 3′ flap (lanes 7–9), and four-way junction (lanes 10–12) substrates, shown diagrammatically at the top of the figure. The flaps on the branched substrates were 16 nt in length; for other details on the substrates see Materials and Methods. Reactions contained either 2 mM MgCl2 (+) or 0.5 mM EDTA (−) and were separated in 0.7% agarose gels. (B) Gel mobility shift assays were performed as in A with 25 ng of full-length Brca1 on the 32P-labeled flap substrate. Varying amounts of unlabeled competitor DNAs were also present from the start of the reactions. Linear duplex DNA was added in lanes 2–5, four-way junctions in lanes 7–10, and supercoiled plasmid DNA in lanes 12–15. The amounts of competitor were varied from 1.56 ng to 100 ng, as indicated. The arrow identifies an additional band formed when unlabeled plasmid is present in the binding reaction, suggesting that both the labeled DNA substrate and unlabeled plasmid DNA are present in the complex. (C) Quantitative comparison of Brca1 DNA binding to the branched substrate in the presence of various DNA competitors. The amounts of protein–DNA complex II formed in the presence of linear, branched, four-way junction, supercoiled plasmid, and linearized plasmid competitors are shown in relation to the total amount of labeled substrate present in each reaction. (D) Gel mobility shift assays were performed as in A on three different lengths of 32P-labeled linear DNA fragments, as indicated at the top of the figure. The amounts of full-length Brca1 present in the reactions were 0.9 ng (lanes 2, 8, 14), 1.8 ng (lanes 3, 9, 15), 3.75 ng (lanes 4, 10, 16), 7.5 ng (5, 11, 17), and 15 ng (lanes 6, 12, 18).