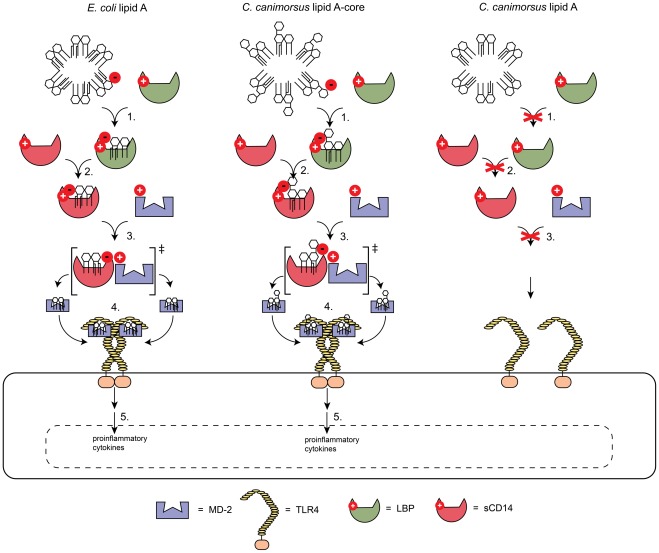
Figure 8. Proposed model for the implication of the LPS core or the 4′ phosphate in enabling the binding to MD-2.
Ionic interactions or hydrogen bonds involving the 4′ phosphate or the Kdo carboxy group in LPS lacking a 4′ phosphate enable the binding of lipid A to either LBP (1.), soluble CD14 (sCD14) (2.) or via an intermediate state to MD-2 (3.). Dependent on the type of lipid A bound to MD-2 this leads to TLR4 multimerization (4.), a downstream signaling cascade and finally release of proinflammatory cytokines (5.).