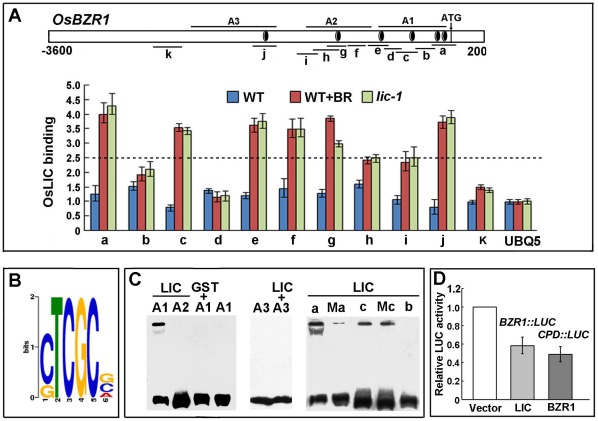
Figure 7. LIC binds to BZR1 and represses its transcriptional expression.
(A) ChIP assay to illustrate LIC binding to the BZR1 promoter. The binding was enhanced in the lic-1 mutant and in wild-type plants treated with BR. The black circles with a white ring indicate the putative binding motif S (CTCGC). A1, A2 and A3, the probes used in EMSA; a–k, sequences tested in ChIP assay; a–c, also as sub-sequences of A1 used in EMSA. The UBQUITIN5 promoter was a control. (B) Putative binding motif S predicted by MEME software (http://meme.sdsc.edu/meme/cgi-bin/meme.cgi). Sequence logo shows the frequencies relative to the information content at each position. (C) Gel shift assay to illustrate LIC binding to the putative core binding sequence. LIC bound to the BZR1 promoter A1 fragment (4 elements) but not to the A2 or A3 fragments (one element); GST could not bind to A1. The right panel shows LIC binding to sub-sequences of the A1 fragment a–c, Ma and Mc (CTCGC were mutated to AAAAA ). (D) Transient transfection assay indicating that LIC inhibits BZR1pro:LUC reporter gene expression in Arabidopsis protoplasts. The AtCPDpro:LUC reporter gene repressed by BZR1 was the control. Data are mean±SD of triplicate experiments.