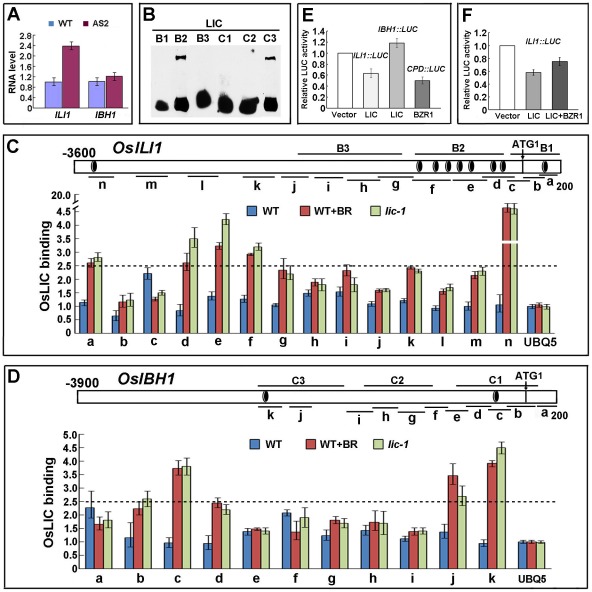
Figure 8. Opposite regulation of downstream genes in BR signaling by LIC and BZR1.
(A) Transcriptional expression patterns of ILI1 and IBH1 in the LIC antisense line (AS2). Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). (B) Gel shift assay to illustrate LIC binding to the different fragments of the ILI1 and IBH1 promoters. ILI1 B2 and IBH1 C3 contain the binding element S. ILI1 B1, B3, IBH1 C1 or C2 fragments contain no or less binding elements. (C) and (D) ChIP analysis of LIC binding to the ILI1 and IBH1 promoters by use of anti-LIC antibody. The binding was enhanced in the lic-1 mutant and in wild-type plants in the presence of BR. The black circle with white ring indicates the binding element S. B1–3 and C1–3 are the probes used in (B), and a–n (used in (C)) and a–k (used in (D)) indicate the sequences tested in ChIP assay. The UBQUITIN5 promoter was used as a control. (E) Transient transfection assay to illustrate that LIC repressed ILI1pro:LUC and activated IBH1pro:LUC reporter gene expression in Arabidopsis protoplasts (the 403-bp ILI1 promoter indicated as B2 in (C) and the 451-bp IBH1 promoter indicated as C3 in (D) were used). The inhibition of AtCPDpro:LUC reporter gene expression by BZR1 was the control. Data are mean± SD. (F) Transient transfection assay indicated that LIC and BZR1 antagonistically regulate ILI1pro:LUC reporter gene expression. Data are mean ± SD.