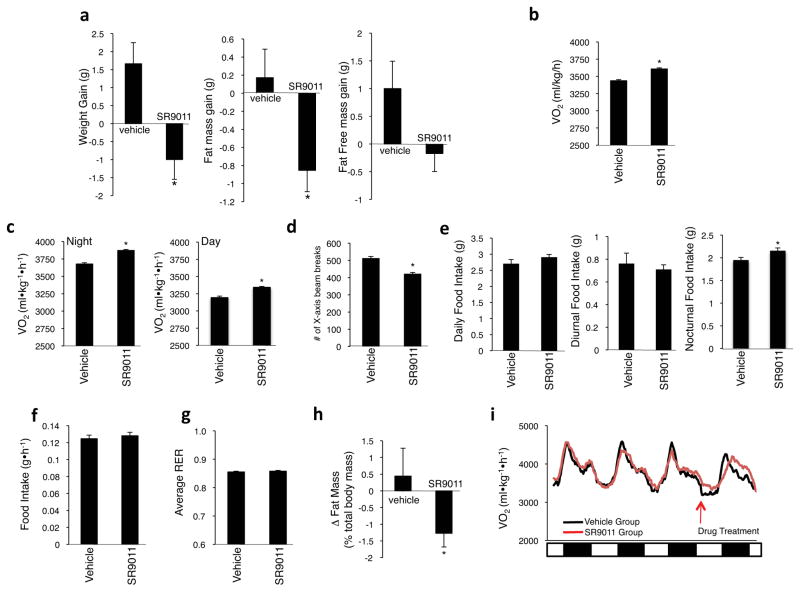
Figure 3. Activation of REV-ERB by SR9011 in vivo results in an increase in energy expenditure and weight loss.
a, Treatment of mice (Balb/c) with SR9011 results in weight loss and fat mass loss. Animals were dosed with SR9011 (100mg/kg, i.p., b.i.d.) for 12 days. b, Oxygen consumption (VO2) is increased in mice treated with SR9011. Results were obtained in using CLAMS and C57Bl6 mice were dosed as described in a except that the duration of treatment was 10 days. c, Oxygen consumption (VO2) is increased during both the diurnal and nocturnal phases of C57Bl6 mice when they are treated with SR9011. Data obtained from the experiment described in b was analyzed for time of day differences. d, Mice treated with SR9011 are less active in the CLAMS as detected by the number of x-axis beam breaks. e, Total daily, diurnal and nocturnal food intake from the animals in the CLAMS study. f, The rate of food intake is not altered by SR9011 treatment. g, Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) is not altered by SR9011 treatment. h, After completion of the 10-day CLAMS experiment animals fat mass was assessed by DEXA. i, Results from a CLAMS experiment illustrating the diurnal increase in oxygen consumption prior to and immediately after administration of SR9011. Note the ~3h delay in the diurnal peak in VO2 following administration of SR9011. For all b.i.d. dosing animals were dosed at CT0 and CT12. * indicates p<0.05. Error bars indicate mean ± s.e.m. and n=6–10 mice