Figure 6.
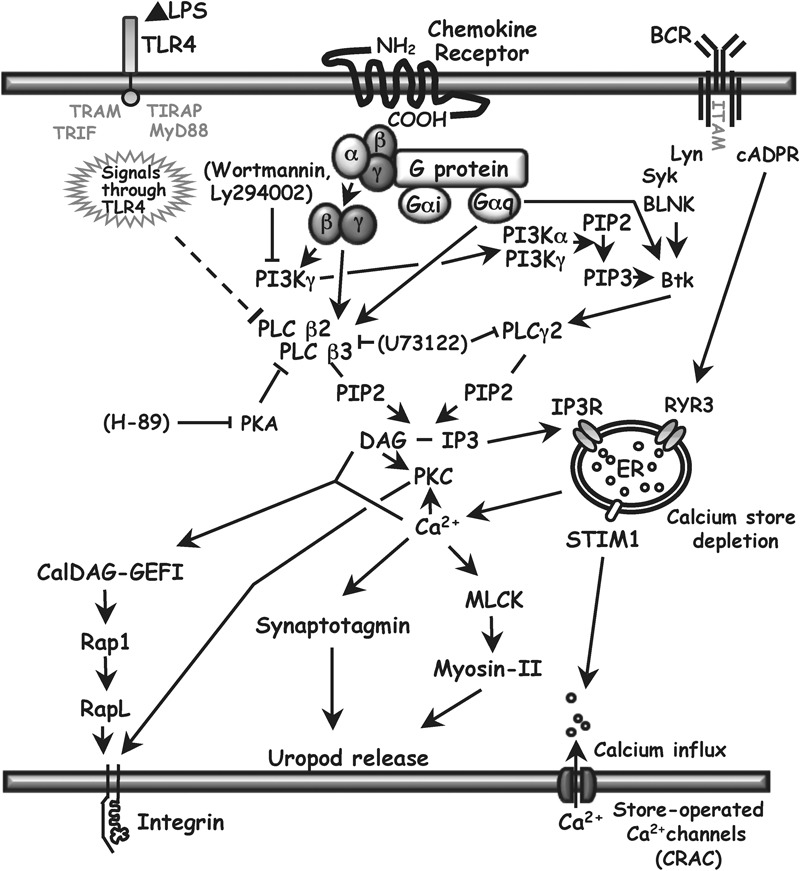
PLC signaling in B cells. The principal isoforms of PLC-β in hematopoietic cells are PLC-β2 and PLC-β3. They can be activated by βγ-dimers or Gα subunits of the Gq family of heterotrimeric G proteins that are coupled to seven transmembrane receptors. PLC-βs can be inhibited by PKA, and expression of PLC-β2 can be downregulated by LPS (this report), which signals through TLR4. PLC converts PIP2 to DAG and IP3. IP3 binding to the IP3R on the ER leads to a rise in cytoplasmic calcium by the release of calcium from ER stores and, indirectly, by opening store-operated plasma membrane calcium channels, the major ones being CRAC. DAG and IP3 can also be produced by PLC-γ2, activated primarily through signals from the BCR. There is an alternate calcium release pathway from BCR through cADPR to RYR3 in the ER. There is a possible cross-talk pathway from G protein through PI3Kγ, PIP3 and Bruton's tyrosine kinase to activate PLC-γ2, but we found that inhibiting PI3K with wortmannin or Ly294002 had no effect on chemokine-induced calcium flux (see text). DAG, together with calcium, can bind to the GEF CalDAG-GEFI, leading to integrin activation. DAG can also enhance integrin avidity for adhesion proteins through a PKC-dependent pathway. Calcium has roles in uropod release at the back of migrating cells by contributing to the activation of myosin II and the activity of synaptotagmins, which are important for lysosome fusion. Arrows show positive effects. Solid lines ending in bars show inhibitory effects. Pharmacological inhibitors used in this study are shown in brackets. Downregulation of PLC-β2 demonstrated in this study is shown using the dashed line. For relevant references, see text and Refs. 52 and 53. BCR, B-cell receptor; cADPR, cyclic ADP ribose; CRAC, calcium release-activated calcium channels; DAG, diacylglycerol; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; IP3R, inositol trisphosphate receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; RYR3, ryanodine receptor 3; STIM1, stromal interaction molecule 1; TLR, Toll-like receptor.
