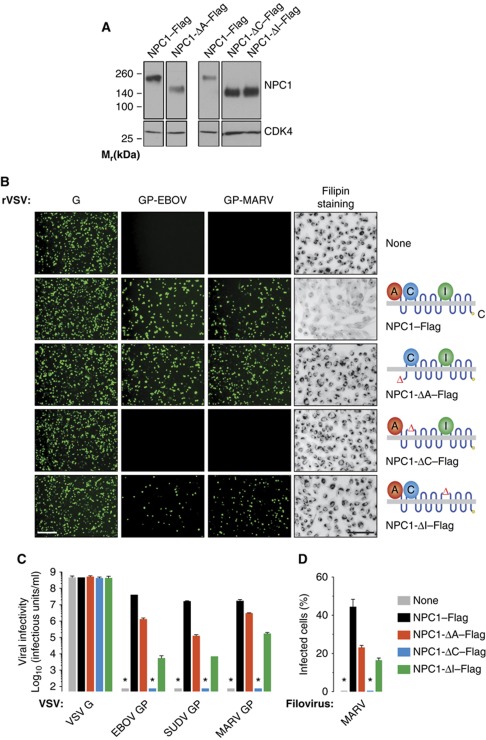
Figure 2.
NPC1 luminal loop domain C is required for filovirus entry, but full-length NPC1 is dispensable. (A) NPC1-null CHO CT43 cells were engineered to express mutant forms of human NPC1–Flag lacking domains A, C, or I. NPC1 expression was determined by IB with an anti-Flag antibody. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) in each sample was detected by IB (Abcam) and provided a loading control. Samples for IB of each NPC1 mutant and its paired WT NPC1 control were resolved on the same gel. NPC1 and CDK4 were detected on separate gels. (B) Capacity of mutant NPC1 proteins to rescue viral entry and transport lysosomal cholesterol. (Left) Infection of NPC1-null CHO CT43 cells expressing mutant NPC1–Flag proteins by recombinant VSVs bearing VSV G or filovirus glycoproteins. Infected cells (green) were visualized by fluorescence microscopy. (Right) Cholesterol clearance by mutant NPC1–Flag proteins in CT43 cells was determined by filipin staining and fluorescence microscopy. Images were inverted for clarity. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C, D) Infectivity of VSV pseudotypes bearing VSV or filovirus glycoproteins (C) and wild-type MARV (D) in CT43 cells expressing mutant NPC–Flag proteins. SUDV, Sudan virus. Results in (C) (n=4–6) are from two independent experiments. Results in (D) (n=3) are from a representative experiment. Error bars indicate s.d. Asterisks indicate values below the limit of detection. Figure source data can be found in Supplementary data.