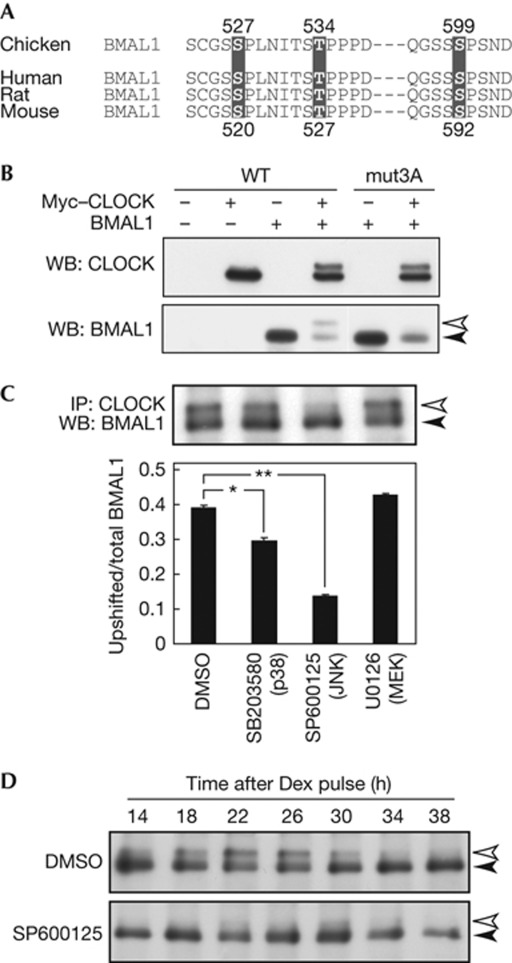
Figure 1.
Effects of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor SP600125 on BMAL1 phosphorylation. (A) The protein sequence around in vitro phosphorylation sites of chicken BMAL1 was aligned with the corresponding regions of mouse, rat and human BMAL1. (B) NIH3T3 cells were transfected with Myc–CLOCK/pSG5 and BMAL1/pcDNA3.1, and the cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis. Ser 520, Thr 527 and Ser 592 in mouse BMAL1 were mutated to Ala (mut3A). (C) NIH3T3 cells were treated for 24 h with indicated inhibitors (20 μM). Data are means with s.e.m. (n=3). Single and double asterisks indicate P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively (Student's t-test, versus DMSO). (D) NIH3T3 cells were treated with dexamethasone (Dex) to synchronize the cellular rhythm. After 2-h incubation, the medium was changed to normal culture medium with 20 μM SP600125 or DMSO (control) and this time point was defined as time 0. The cells were collected at indicated time points. (C,D) The total protein extracts of the cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-CLOCK mAb, followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-BMAL1 mAb. DMSO, dimethylsulphoxide; IP, immunoprecipitation; mAb, monoclonal antibody; WB, western blot; WT, wild type.