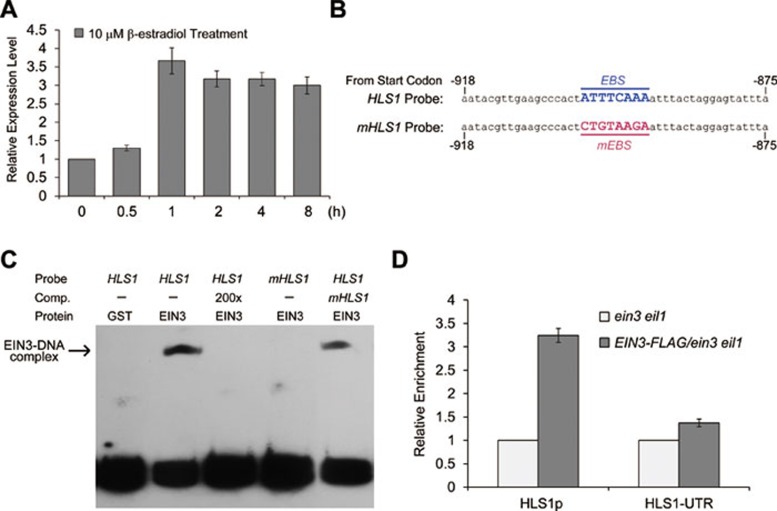
Figure 5.
HLS1 is a direct target gene of EIN3. (A) Rapid induction of HLS1 expression in iE/ein3 eil1 by estradiol. 3-day-old etiolated iE/ein3 eil1 (a transgenic plant inducibly expressing EIN3-FLAG in the ein3 eil1 background) seedlings grown on MS medium were treated with 10 μM estradiol for indicated hours before the seedlings were collected for RNA extraction. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (B) Oligonucleotides used in the EMSA assays. The HLS1 probe contains an EBS motif (underlined), which is a putative EBS. In the mHLS1 probe, the EBS was mutated to mEBS (underlined). Number showed the location upstream of the start codon. (C) EMSA results showing in vitro binding of GST-EIN3 to the EBS motif in the promoter of HLS1. Protein-DNA complexes were detected when GST-EIN3 was incubated with labeled HLS1 probe, and competition assays were conducted by adding 200-fold excessive unlabeled HLS1 or mHLS1 probe. GST-EIN3 was also incubated with labeled mHLS1 probe and no protein-DNA complexes were observed. (D) ChIP assays indicating in vivo binding of EIN3 to the HLS1 promoter sequence. Chromatin from ein3 eil1 and transgenic plants constitutively expressing EIN3-FLAG in ein3 eil1 was immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody, and the quantification of the indicated DNA fragments in the precipitated chromatin was determined by quantitative real-time PCR. The amounts of DNA amplified from the EIN3-FLAG/ein3 eil1 seedlings were normalized to that from ein3 eil1 plants. The 3′-UTR fragment of HLS1 was used as a negative control. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.