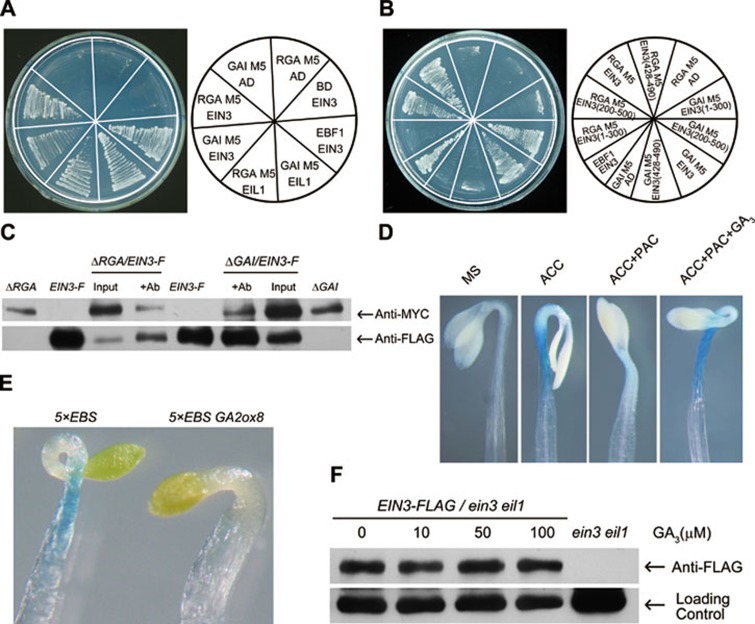
Figure 6.
RGA/GAI interacts with EIN3/EIL1 and inhibits their function. (A) RGA/GAI interacted with EIN3/EIL1 in yeast cells. RGA M5 fragment (aa 209-587) and GAI M5 fragment (aa 158-533) were used in the yeast two-hybrid assays. EBF1/EIN3 interaction was used as a positive control. (B) EIN3 fragment (aa 200-500) was sufficient for the interactions with RGA and GAI in yeast cells. (C) Co-IP assays showing RGA/GAI association with EIN3 in vivo. EIN3-FLAG/ein3 eil1 (EIN3-F) was crossed with 35S:TAP-RGAΔ17 (ΔRGA) or 35S:TAP-GAIΔ17 (ΔGAI), and F1 plants were used for Co-IP. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2 agarose beads (+Ab) and detected with either anti-MYC or anti-FLAG antibodies. (D) PAC treatment inhibited the ACC-induced 5×EBS:GUS expression. 3-day-old etiolated 5×EBS:GUS seedlings grown on the indicated medium (ACC: 10 μM, PAC: 1 μM, and GA: 10 μM) were used for GUS staining. (E) Expression of 35S:GA2ox8 in the 5×EBS:GUS background decreased the ACC-induced GUS staining. 3-day-old etiolated 5×EBS-GUS and 35S:GA2ox8 5×EBS-GUS seedlings grown on 10 μM ACC medium were used for GUS staining. (F) GA3 treatment did not affect the protein level of EIN3 in EIN3-FLAG/ein3 eil1. 3-day-old etiolated seedlings grown on 0.2 μM PAC were treated with indicated concentrations of GA3 for 4 h before proteins were extracted for immunoblot assay with anti-FLAG antibody.