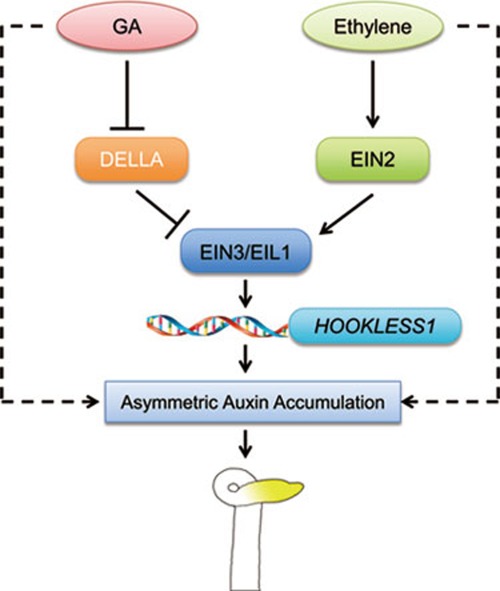
Figure 8.
A proposed model of GAs and ethylene co-action in promoting the hook curvature. GAs and ethylene cooperatively regulate the hook curvature partly by inducing the gene expression of HLS1, a putative N-acetyltransferase essential for hook formation. EIN3/EIL1 are the integration node linking the two hormone pathways to directly activate the HLS1 transcription, in which ethylene stabilizes EIN3/EIL1, while GAs relieve the repression of DELLA proteins on EIN3/EIL1. Meanwhile, GAs and ethylene also initiate the HLS1-independent pathways to regulate hook curvature, probably by modulating asymmetric auxin accumulation in the hook region. The solid lines indicate proved regulations, whereas the dotted lines indicate proposed regulations.