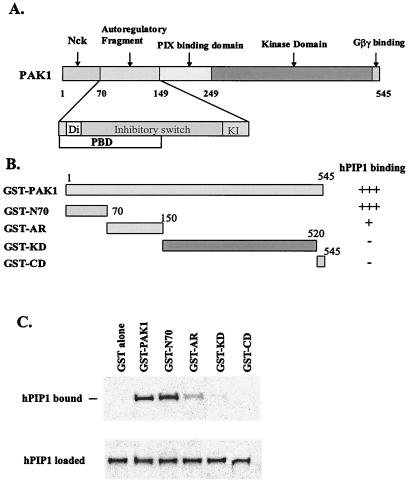
Figure 6.
Identification of PAK1 domain(s) responsible for the interaction with hPIP1. (A) Domain structure of the PAK1 polypeptide chain. The N terminus (residues 1–69) was identified as interacting with Nck. The autoregulatory regions (residues 70–149) contain the dimerization segment (Di), the p21 binding domain (PBD), the inhibitory switch domain (IS), and the kinase inhibitory segment (KI). The C terminus contains the kinase domain and the Gβγ-binding motif. (B) GST-PAK1 fusion proteins. Numerals indicate residue numbers at the boundaries of various subdivisions. (C) Interaction of different GST-PAK1 domains with in vitro translated hPIP1. HPIP1 interacts with the full length PAK1, the N-terminal domain (residues 1–70), and the autoregulatory domain (residues 70–149). The PIX-binding domain and the C-terminal region, including the kinase domain and the Gβγ-binding motif, are not involved in the hPIP1 association. Bottom band shows that the same amount of 35S-labeled hPIP1 was used in the binding assays.