Figure 1.
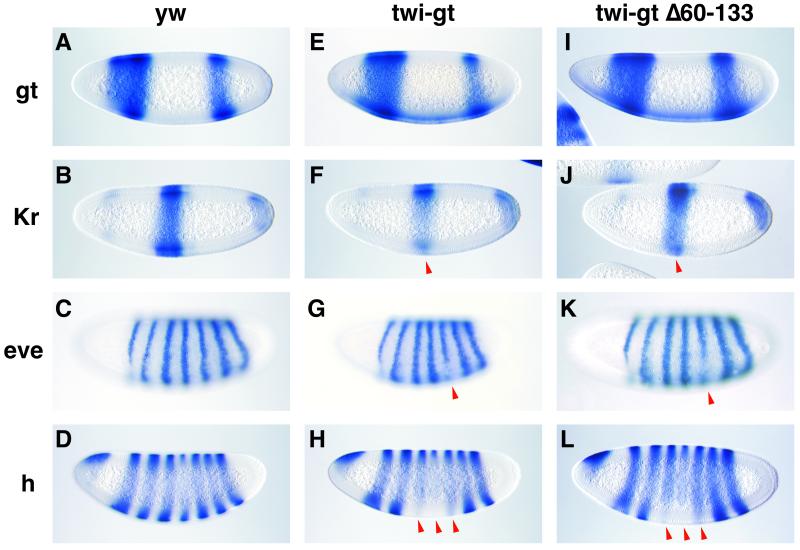
Giant represses Krüppel, eve, and hairy expression. Wild-type and transgenic embryos were hybridized with the indicated digoxigenin-labeled antisense RNA probes (see labels to the left of A–D) and are oriented with anterior to the left and dorsal up. (A, E, I) giant (gt) staining patterns in precellular wild-type (yellow;white; yw; A), and transgenic embryos (E and I) that exhibit low levels of giant in ventral regions by using the modified twi enhancer. The wild-type and mutant giant RNAs (twi-gt and twi-gtΔ60–133) are expressed at comparable levels. All three strains exhibit strong staining in anterior and posterior regions, which represent the normal sites of giant expression. (B, F, J) Krüppel (Kr) staining patterns in wild-type (B) and transgenic cellularized embryos that express either the wild-type giant RNA (F) or the mutant RNA lacking the putative repression domain (J). Normally, Krüppel is uniformly expressed in dorsal and ventral regions (B). However, ectopic Giant leads to attenuated expression in ventral regions (arrowheads, F and J). Both forms of Giant are equally effective at repressing Krüppel. (C, G, K) eve staining patterns in wild-type (C) and transgenic embryos (G, K). Both twi-giant transgenes lead to the repression of eve stripe 5 in ventral regions (arrowheads, G and K). (D, H, L) hairy (h) staining patterns in wild-type (D) and transgenic embryos (H, L). Both twi-giant transgenes lead to the repression of hairy stripes 3, 4, and 5.