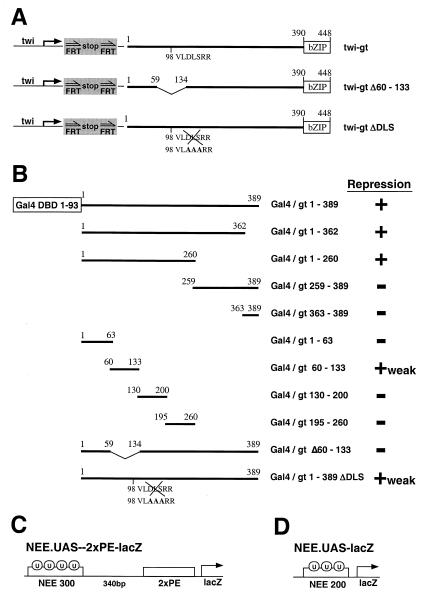
Figure 3.
Summary of expression vectors and reporter genes. (A) The Giant protein is composed of 448-aa residues, and includes a bZIP DNA-binding domain at the carboxy terminus (Top). Two tandem copies of a modified twist PE enhancer (PEeEt; “twi”) were used to misexpress three different forms of the giant coding sequence in ventral regions of transgenic embryos: wild type, a mutant form lacking amino acid residues 60–133, and a mutant form containing alanine substitutions in the putative repression motif, VLDLS. Both mutant transgenes are as effective as the wild-type coding sequence in repressing eve stripe 5 and hairy stripes 3, 4, and 5. (B) Previous studies have shown that Giant repression activity is mediated by the first 389-aa residues in the absence of the bZIP domain. This extended region contains a sequence that is reminiscent of the dCtBP interaction motif, VLDLSRR starting at position 98. A variety of Gal4-Giant fusion proteins were expressed in central regions of transgenic embryos by using Krüppel 5′ cis-regulatory DNA. Mutations in the VLDLSRR motif impair the repression activity of an otherwise normal, “full-length” 1–389 Gal4-Giant fusion protein. Full repression activity is obtained with an N-terminal sequence spanning amino acid residues 1–260. Neither carboxyl-terminal peptide displayed repression activity in the transgenic embryo assays (see Fig. 4). The analysis of smaller amino-terminal peptides identified 60–133 as the minimal Gal4-Giant fusion protein that retained repression activity. Removal of this sequence from the full-length fusion protein eliminated repression activity. Alanine substitutions in the VLDLS motif attenuate the repression activity of a full-length Gal4-Giant fusion protein. (C) Reporter gene used to examine the short-range activities of Gal4-Giant fusion proteins. The lacZ reporter gene was placed under the control of two enhancers: a modified 300-bp rhomboid NEE lateral stripe enhancer placed upstream of two tandem copies of the 250-bp twist PE sequence. The NEE and PE enhancers are separated by a 340-bp spacer sequence. The NEE contains 4 UAS sequences (“u”) that permit binding of Gal4-Giant proteins. (D) The second reporter gene used for the analysis of Gal4-Giant fusion proteins contains a minimal 200-bp rhomboid NEE with three UAS sites.