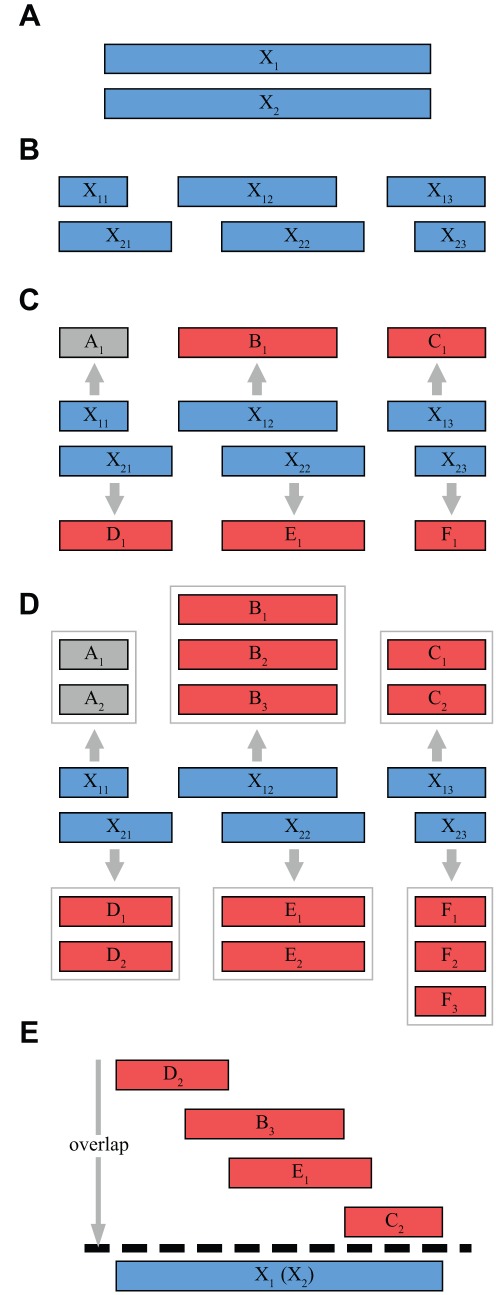
Figure 2. Schematic of the proposed sequencing method.
The target sequence X is replicated multiple times (A) and the different replicas  with
with  are randomly separated into fragments
are randomly separated into fragments  (B). Sequencing each fragment using classical SBH yields one possible ‘candidate’
(B). Sequencing each fragment using classical SBH yields one possible ‘candidate’  for each fragment’s sequence (C). Using the repeat structure of the candidate, the complete set of possible fragment sequences is constructed (D). Aligning the candidates allows to uniquely determine the target sequence and choose one element of each candidate set (E). The method is robust against erroneous candidate sets resulting from errors in the determined probe spectra of fragments, indicated as grey bars in (D).
for each fragment’s sequence (C). Using the repeat structure of the candidate, the complete set of possible fragment sequences is constructed (D). Aligning the candidates allows to uniquely determine the target sequence and choose one element of each candidate set (E). The method is robust against erroneous candidate sets resulting from errors in the determined probe spectra of fragments, indicated as grey bars in (D).