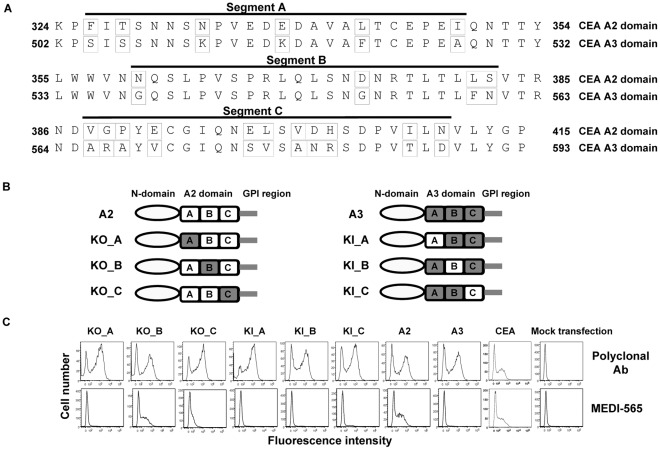
Figure 4. Swap-mutants of human CEA.
A, amino acid sequence alignment of the A2 and A3 domains of CEA. Sequence homology analysis revealed 21 amino acids that differed between these two domains (amino acids boxed). Three segments, A, B, and C, were defined in the A2 and A3 domains to generate swap-mutants. B, a schematic display of swap mutants that were constructed by exchanging segments A, B, or C between the A2 (open boxes) and A3 (grey boxes) domains using the truncated mutant A2 or A3 as a template which encodes the N-domain, the A2 or A3 domain, and the GPI region. C, flow cytometry analysis of binding of MEDI-565 to deletion mutants expressed on the surface of HEK293 F cells. All mutants were expressed well as monitored by anti-CEA polyclonal antibody. MEDI-565 did not bind well to any of the knock-out (KO) or knock-in (KI) mutants which lack either the A or C segment of the A2 domain (KO_A, KO_C, KI_A, KI_B and KI_C), but bound well to the one variant which encoded both the A and C segments of the A2 domain (KO_B).