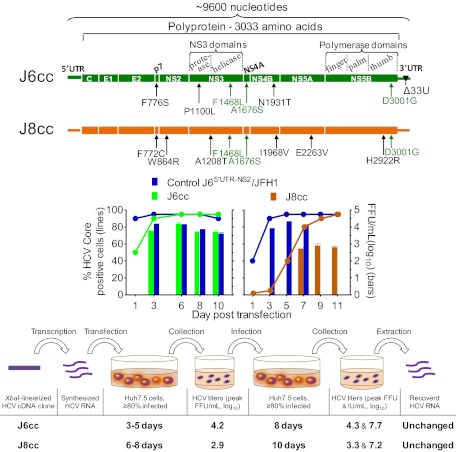
Fig. P1.
Efficient full-length HCV genotype 2a (J6cc) and 2b (J8cc) infectious culture systems. (Top) The diagram shows the HCV J6cc and J8cc genomes; cell culture-adaptive mutations are shown. Functional domains in NS3 and three structural domains in NS5B are indicated. Green lettering indicates the three J6-derived key mutations (F1468L/A1676S/D3001G, abbreviated LSG) that enabled J6 and J8 genomes to replicate and grow in human Huh7.5 cells. (Middle) We scored the percentage of HCV-positive cells (Left y axis) (5). When ≥80% of cells were infected, culture fluid was collected, and the number of infectious virus particles per milliliter of fluid was determined (FFU/mL) (Right y axis). (Bottom) The collected culture fluid was used to infect naive Huh7.5 cells (passage); the culture fluid was collected, and HCV infectivity (FFU/ml) and HCV RNA (IU/ml) titers were determined. The entire genome sequence of recovered viral RNA was analyzed; no sequence changes were found, indicating the genomes are genetically stable.