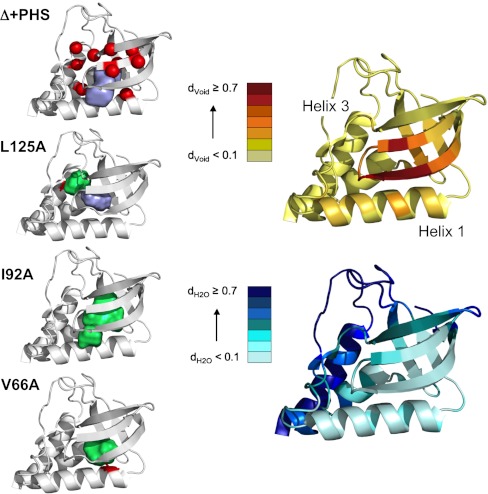
Fig. 1.
Structures of Δ + PHS SNase and cavity-containing variants. Left Panel, from Top to Bottom: Structure of Δ + PHS SNase (3BDC) with the Cα positions of the 10 cavity-containing variants indicated with red spheres and with the surface representation of the central cavity in purple. Cavity volume was calculated using a 1.1 Å sphere and McVol (11). Structures of the cavity mutants L125A (3NXW), I92A (3MEH) and V66A (3NQT) with the engineered cavities in green and the mutated residue in red. Right Panel: Estimation of the void density (Top) and hydration density (Bottom) for each Cα position of the Δ + PHS reference protein. See SI Materials and Methods in SI Appendix and (9) for the details concerning calculation of void and hydration density. Briefly, the 1,000 configurations resulting from a 10 ns all-atom MD simulation in explicit solvent were submitted to Monte Carlo point oversampling. All points that fell within the structure and not on an atom of solvent or the protein were counted for void density. Water density was calculated as the number of oxygen atoms of water molecules within 5 Å of each Cα carbon, normalized to the largest number found for a Cα carbon.