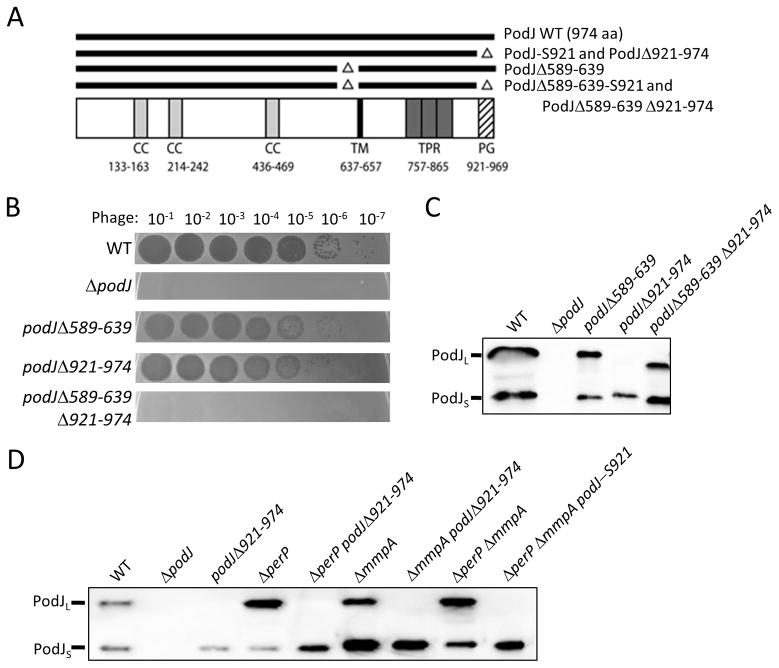
Figure 1.
Two deletions in podJ abolish phage sensivity. A: Schematic of PodJ, with predicted coiled coil (CC), transmembrane (TM), tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) and peptidoglycan binding (PG) domains indicated. The numbers above the predicted domain indicate the amino acid region for each domain. Important mutants used in this study are depicted as lines above the schematic. B: Phage sensitivity assays of various podJ mutants. Cell cultures were OD600 normalized then mixed with soft agar and plated on agarose plates. After hardening, serial dilutions of bacteriophage ΦCbK were spotted onto the plates and allowed to dry prior to incubation. C: Western analysis of various podJ mutants. Western analysis was performed using whole cell lysates from OD600 normalized cell cultures and anti-sera raised against the cytoplasmic portion of PodJ to show PodJL and PodJS. D: Western analysis of the fast processing podJΔ921-974 allele in combination with protease mutants. Western analysis was performed using whole cell lysates from OD600 normalized cell cultures and anti-sera raised against the cytoplasmic portion of PodJ to show PodJL and PodJS. ΔperPΔmmpA podJ-S921 used a stop codon at the amino acid 921 codon to remove the C-terminal 53 amino acids of PodJ and results in the synthesis of the same protein as the podJΔ921-974 mutant.