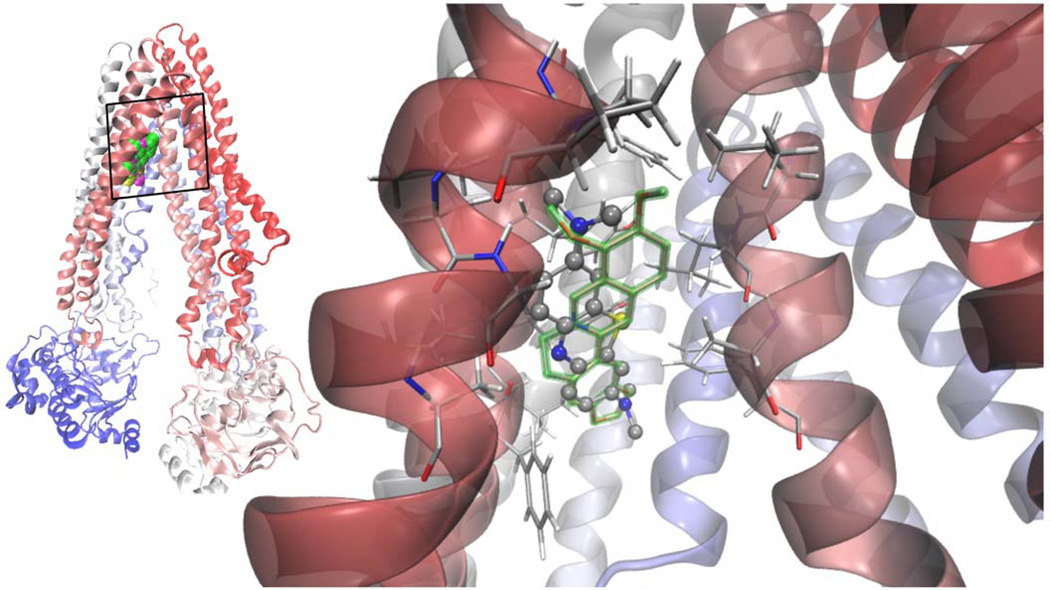
Figure 2.
Left: superimposed Van der Waals (VdW) models of the lowest energy docked structures of berberine [75] TBO (yellow) and MB (magenta) in apex of the inverted "V" depicted by the transmembrane α-helices 4 and 6 as they separate from top to bottom (in this orientation the extracellular side at the top; cartoon representation of the protein colored according to the sequence, from red to blue). Right: MB showed a clear specificity for the site overlapping with berberine, the calculated binding energies being practically indistinguishable. The hydrophobic pocket of negative electrostatic potential is rich in hydrophobic and aromatic residues, mainly form helices 4, 5 and 6.
The structure of the dyes were optimized with the method for fundamental vibrational frequencies B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p level of theory using the gaussian03 [129] package in a model polar solvent (PCM acetonitrile) [130]. The structures were docked onto the whole chamber formed by the twelve Transmembrane Domains (TMs) of the protein at the height to which they span the cell membrane in order to locate their binding sites, using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm implemented in Autodock 4.2.3. Afterwards, the whole protocol was applied in a smaller region comprising their main binding site. Their highly delocalized charge distribution was modeled from the QM results instead of the default program charges [131].