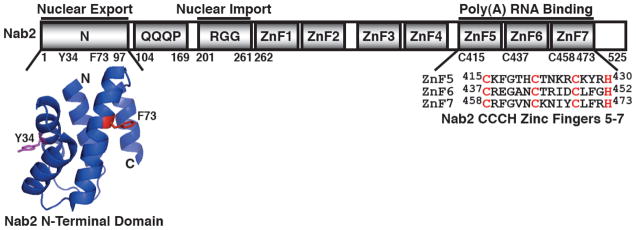
Fig. 1. Functional domains of Nab2.
Nab2 is a 525 residue protein that possesses four key domains: an N-terminal domain (residues 1-97), a Q-rich domain (residues 104-169), an RGG domain (residues 201-261), and C-terminal tandem zinc finger domain (residues 262-473). The N-terminal domain of Nab2 (Nab2-N) facilitates nuclear export of poly(A) RNA and interacts with nuclear pore-associated Mlp1 protein in the nucleus and the nuclear rim-associated Gfd1 protein in the cytoplasm (20,22,28,30). The crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of Nab2 reveals that Nab2-N forms a five alpha-helix bundle with a proline-tryptophan-isoleucine (PWI)-like fold (20,22). The key residue Phe73 (red) that is important for interaction with Mlp1 and Tyr34 (magenta) that is critical for interaction with Gfd1 are highlighted (22,30,31). The RGG domain mediates interaction with the Nab2 import receptor, Kap104 (20,23–25). The Q-rich domain is not essential and currently has no characterized function (20). The C-terminal zinc finger domain contains seven tandem CCCH-type zinc fingers (ZnF) and mediates specific high affinity binding to polyadenosine RNA (10,20,21,26).