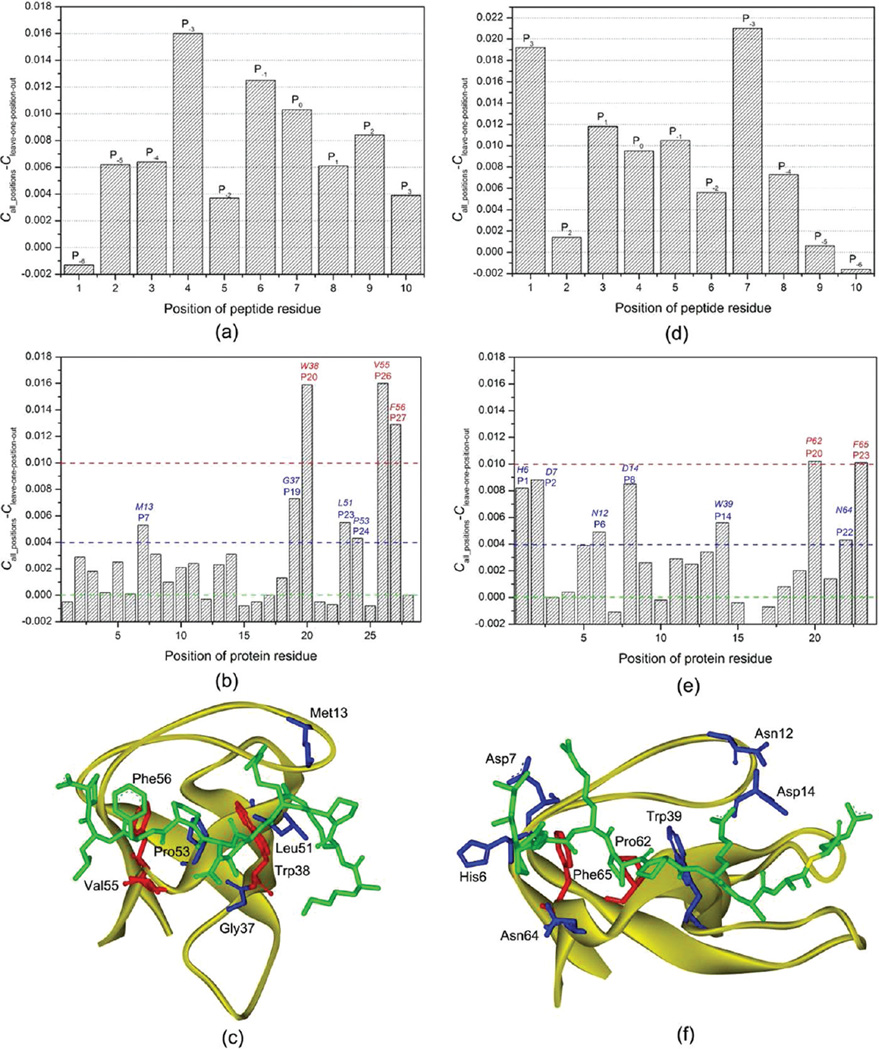
Figure 3.
Contributions of the domain-peptide residues to SH3 binding specificity. (a) hanges of the Matthews correlation coefficients (C) in the leave-one-position-out cross-validation for the class-I peptides. (b) Changes of the Matthews correlation coefficient in the leave-one-position-out cross-validation for the 28 important class-I SH3 domain positions. (c) Spatial locations of the seven SH3 domain positions that have a change of C larger than 0.004 in Boi1. The SH3 domain is shown in strand. The peptide and the domain residues at the important positions are shown in stick. The three residues with a change of C larger than 0.01 are colored in red and the other four important residues in blue. (d) Changes of the Matthews correlation coefficients (C) in the leave-one-position-out cross-validation for the class-II peptides. (e) Changes of the Matthews correlation coefficient in the leave-one-position-out cross-validation for the 24 important class-II SH3 domain positions. (f) Spatial locations of the seven SH3 domain positions that have a change of C larger than 0.004 in Amph. The SH3 domain is shown in strand. The peptide and the domain residues at the important positions are shown in stick. The two residues with a change of C larger than 0.01 are colored in red and the other six important residues in blue.