Abstract
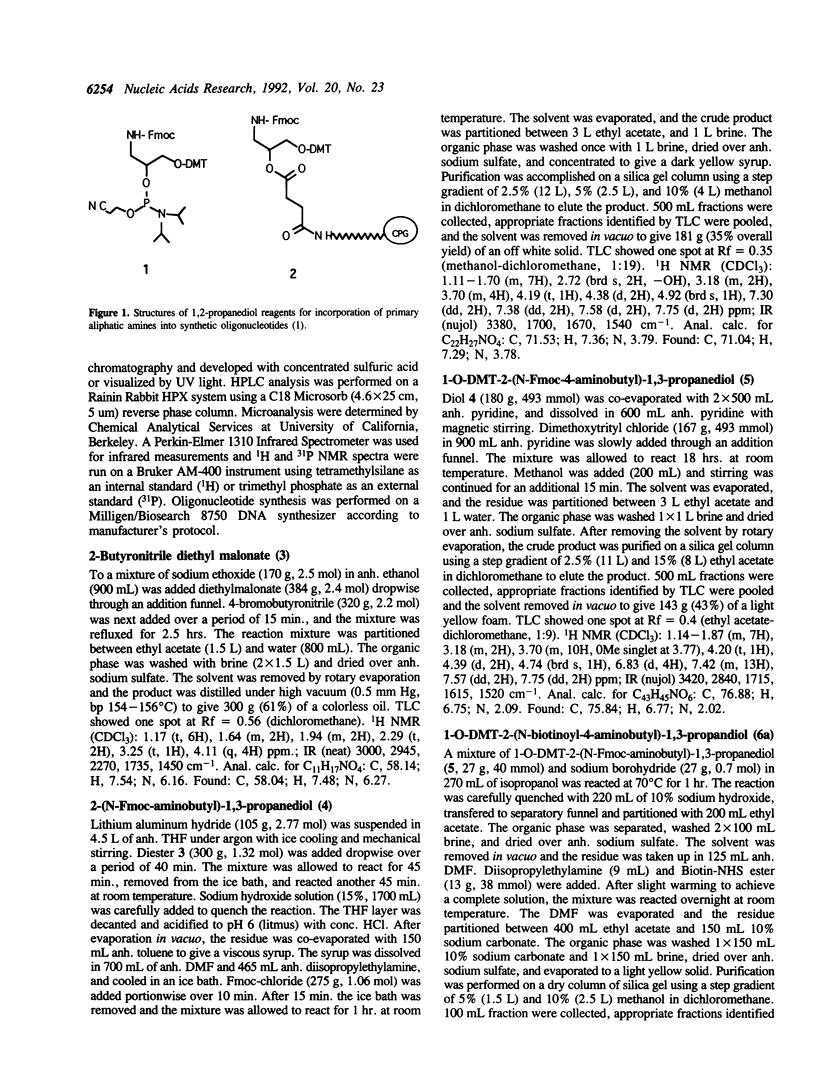
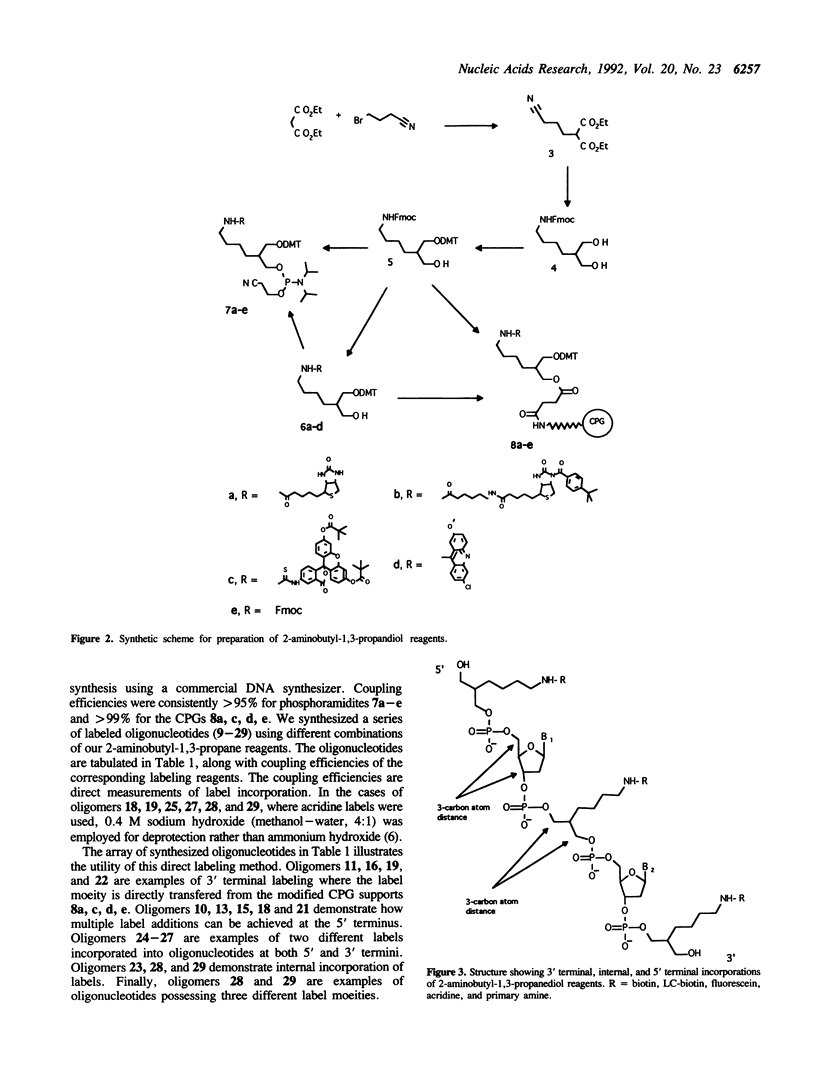
Novel CE-phosphoramidite (7a-e) and CPG (8a, c, d, e) reagents have been prepared from a unique 2-aminobutyl-1,3-propanediol backbone. The reagents have been used to directly label oligonucleotides with fluorescein, acridine, and biotin via automated DNA synthesis. The versatile 2-aminobutyl-1,3-propanediol backbone allows for labeling at any position (5', internal, and 3') during solid phase oligonucleotide synthesis. Multiple labels can be achieved by repetitive coupling cycles. Furthermore, the 3-carbon atom internucleotide phosphate distance is retained when inserted internally. Using this method, individual oligonucleotides possessing two and three different reporter molecules have been prepared.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albretsen C., Kalland K. H., Haukanes B. I., Håvarstein L. S., Kleppe K. Applications of magnetic beads with covalently attached oligonucleotides in hybridization: isolation and detection of specific measles virus mRNA from a crude cell lysate. Anal Biochem. 1990 Aug 15;189(1):40–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge W., Sproat B., Stegemann J., Schwager C., Zenke M. Automated DNA sequencing: ultrasensitive detection of fluorescent bands during electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4593–4602. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birg F., Praseuth D., Zerial A., Thuong N. T., Asseline U., Le Doan T., Hélène C. Inhibition of simian virus 40 DNA replication in CV-1 cells by an oligodeoxynucleotide covalently linked to an intercalating agent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2901–2908. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehab F. F., Kan Y. W. Detection of specific DNA sequences by fluorescence amplification: a color complementation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9178–9182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry G., Lachenmeier E., Mayrand E., Giusti B., Fisher J., Johnston-Dow L., Cathcart R., Finne E., Kilaas L. A new approach to template purification for sequencing applications using paramagnetic particles. Biotechniques. 1992 Jul;13(1):124–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman T., Bergh S., Moks T., Uhlén M. Bidirectional solid-phase sequencing of in vitro-amplified plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):84–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf A., Reckmann B., Pingoud A. Quantitative analysis of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products using primers labeled with biotin and a fluorescent dye. Anal Biochem. 1991 Mar 2;193(2):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90014-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiura K., Durrant I., Evans M. R., Gait M. J. Biotinyl and phosphotyrosinyl phosphoramidite derivatives useful in the incorporation of multiple reporter groups on synthetic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4345–4354. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. S., Frye R. A., Liu E. Bifunctional oligonucleotide probes synthesized using a novel CPG support are able to detect single base pair mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7187–7194. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. S., Sherman-Gold R., Leon R. A new and versatile reagent for incorporating multiple primary aliphatic amines into synthetic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7179–7186. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Taagaard M., Marugg J. E., van Boom J. H., Dahl O. Application of 2-cyanoethyl N,N,N',N'-tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite for in situ preparation of deoxyribonucleoside phosphoramidites and their use in polymer-supported synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7391–7403. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., François J. C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison-Behmoaras T., Roig V., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific intercalating agents: intercalation at specific sequences on duplex DNA via major groove recognition by oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9198–9202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zendegui J. G., Vasquez K. M., Tinsley J. H., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. In vivo stability and kinetics of absorption and disposition of 3' phosphopropyl amine oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):307–314. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



