Figure 4.
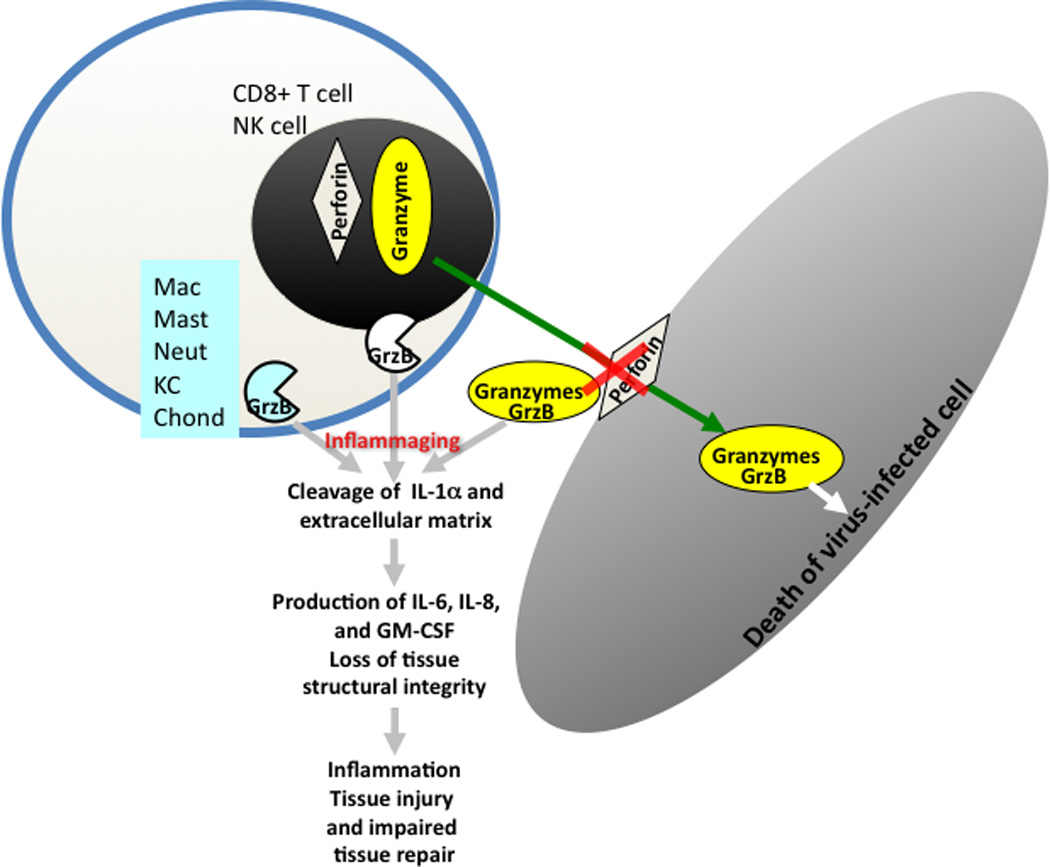
Granzyme B (GrzB) is released by CTL and NK cells to induce apoptosis of virus-infected cells and requires perforin for internalization into cells. Once inside the cell, GrzB induces apoptosis and this is referred to as the classical GrzB/apoptosis pathway. In the absence of perforin, GrzB is released into extracellular space (bGrzB is the biomarker) stimulating GrzB in other cells and causing cleavage of IL-1α and the extracellular matrix causing inflammation and loss of tissue integrity.
