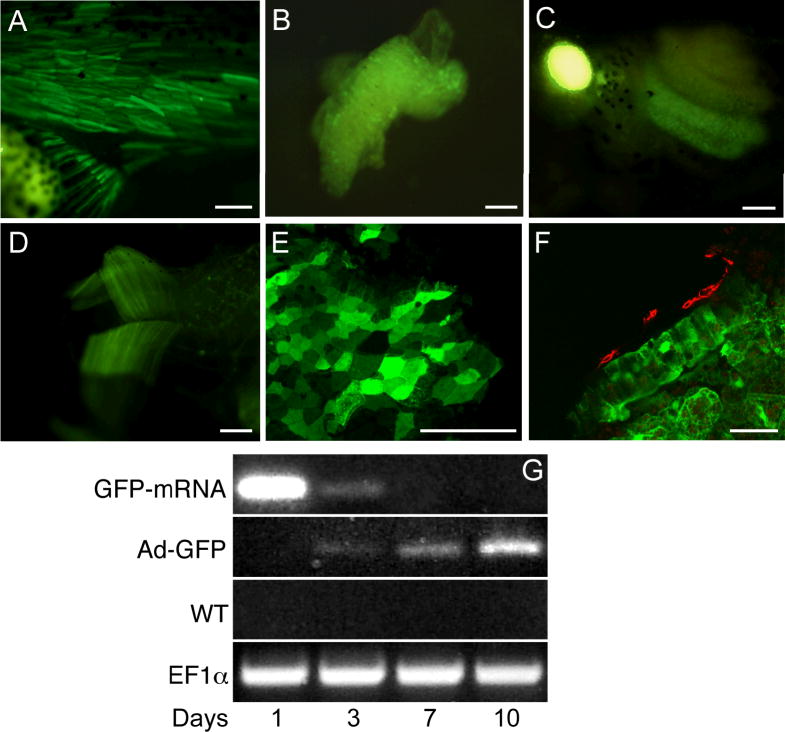
Figure 5. Adeno-GFP infection of Xenopus early embryos.
Embryos were injected with adeno-GFP at the indicated early stage, raised to tadpoles, and photographed for GFP fluorescence at stage 45.
A. Trunk and tail muscle, injected stage 8.
B. Scattered cells in liver, injected stage 8.
C. Small intestine loop, injected stage 14. Bright patch on left is autofluorescence of gall bladder.
D. Jaw muscles, injected stage 10.5.
E. Confocal view of flattened small intestine epithelium, injected stage 14.
F. Transverse confocal view of GFP (green) and smooth muscle actin (red) from small intestine, injected stage 14.
G. RT-PCR of GFP mRNA. Samples are from embryos injected with GFP RNA at 2 cells (top row); embryos injected with adeno-GFP as blastulae (second row); control embryos (third row); loading control (bottom row).
Scale bars indicate 100μm in A-D and 50μm in E-F