Figure 4.
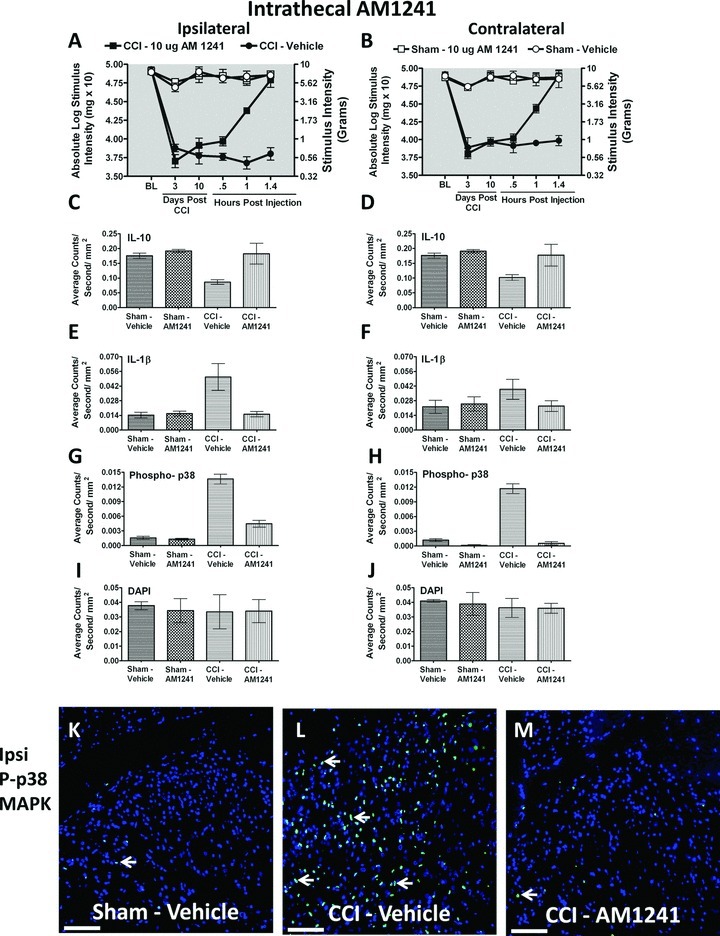
Immunofluorescent intensity quantification from 7-μm thick sections of dorsal horn spinal cord from behaviorally verified rats following i.t. vehicle or AM1241. (A, B) Prior to CCI, all groups exhibited similar ipsilateral and contralateral BL thresholds. CCI produced significant bilateral allodynia at Day 3 and 10 following injury compared to sham-treated animals. Behavioral responses following AM1241 (10 μg) produced maximal bilateral reversal of allodynia followed by tissue collection of immunofluorescent intensity quantification. (C, D) IL-10 expression was bilaterally decreased in CCI-treated rats that received i.t. vehicle compared to control sham-treated rats given either vehicle or AM1241, while IL-10 IR recovered to sham levels in CCI neuropathic rats given i.t. AM1241. (E, F) Compared to sham controls, IL-1β expression was increased ipsilaterally, but not contralaterally in CCI-treated animals given i.t. vehicle of AM1241. However, i.t. AM1241 in CCI-treated rats robustly suppressed increases in IL-1β IR. (G, H) Phospho-p38 expression was bilaterally increased in CCI-induced neuropathic rats treated with i.t vehicle of AM1241. Increased bilateral p-p38MAPK was significantly suppressed in CCI-treated rats given i.t. AM1241. (I, J) No differences in DAPI nuclear stain fluorescent intensity were observed in either sham control or CCI-treated rats given either i.t. vehicle or AM1241. (K, L, and M) Representative spectrally unmixed images at 20× magnification of p-p38 MAPK fluorescent labeling (green) with DAPI nuclear stain (blue). In all images, the scale bar is equal to 50 μm.
