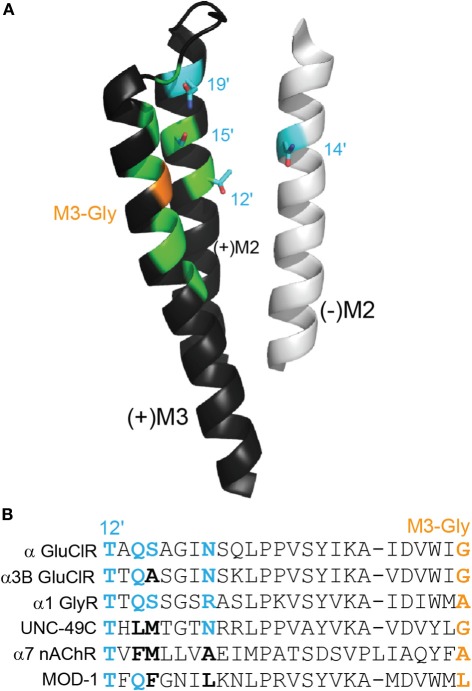
Figure 3.
Polar side chains near the ivermectin benzofuran. (A) (+)M3 and (+)M2 from the principal face and (−)M2 from the complementary face of the ivermectin binding site in the α GluClR from C. elegans, as in Figure 2A. Polar side chains close to the bound ivermectin molecule are shown in cyan. The M3-Gly position crucial to ivermectin sensitivity is shown in orange. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of residues, stretching from M2–12′ to M3-Gly positions. The four cyan side chains from (A) are shown in bold in the alignment, in cyan if polar and in black if neutral. The M3-Gly position is in orange. The α GluClR from C. elegans, the α3B GluClR from H. contortus and the human α1 GlyR are activated by ivermectin Cully et al. (1994); McCavera et al. (2009); Shan et al. (2001), the UNC-49C (co-expressed with UNC-49B) GABA receptor from H. contortus and the human α7 nAChR are not activated but are potentiated by ivermectin (Brown et al., 2012); Krause et al. (1998), and the MOD-1 5-HT receptor from C. elegans is insensitive to ivermectin (Ranganathan et al., 2000).