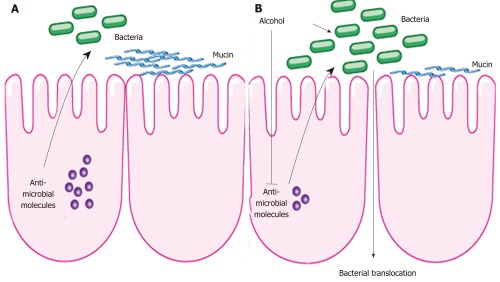
Figure 1.
Intestinal changes following alcohol administration. A: In health, antimicrobial molecules as part of the innate immune response are secreted by intestinal epithelial cells and kill enteric bacteria. B: Alcohol suppresses the expression of these molecules resulting in intestinal bacterial overgrowth and dysbiosis. This might contribute to bacterial translocation observed after alcohol. Alcohol might also exert a direct effect on the intestinal microflora.