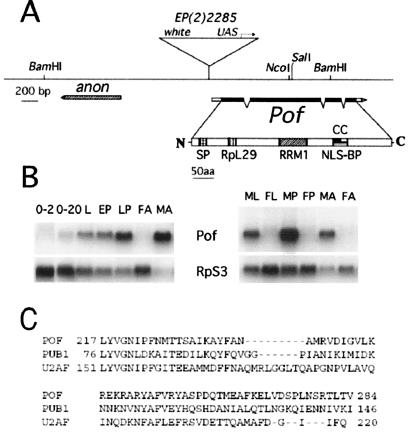
Figure 1.
Map of the Pof gene. (A) The exon-intron structure of the Pof gene (as deduced from various cDNA clones) is shown below the genomic DNA line (derived from the Berkeley Genome Project). Filled boxes represent coding regions, and open boxes represent untranslated sequences. Motifs in the deduced polypeptide sequence are SP, amino acid sequence used for raising antisera; RpL29, Ribosomal protein L29 signature motif (residues 92–107, predicted by genequiz); RRM1, RNA-binding domain (residues 217–284, predicted by pfam); NLS-BP, a bipartite nuclear localization signal (residues 351–367, predicted by psortii); CC, a region likely to form a coiled coil (residues 353–383, predicted by coils). (B) Developmental Northern blot analysis. RNA samples are from 0- to 2-h and 2- to 20-h embryos (0–2, 2–24), third instar larvae (L), early pupae (EP), late pupae (LP), adult females (FA), adult males (MA), third instar male larvae (ML), third instar female larvae (FL), male pupae (MP), and female pupae (FP). The blot was hybridized with a Pof cDNA probe and then reprobed with RpS3 to control RNA loading. (C) Alignment of POF RRM1 domain to RNA-binding domains of PUB1 (yeast) and 65kDa subunit of splicing factor U2AF (human), accession nos. P32588 and P26368, respectively.