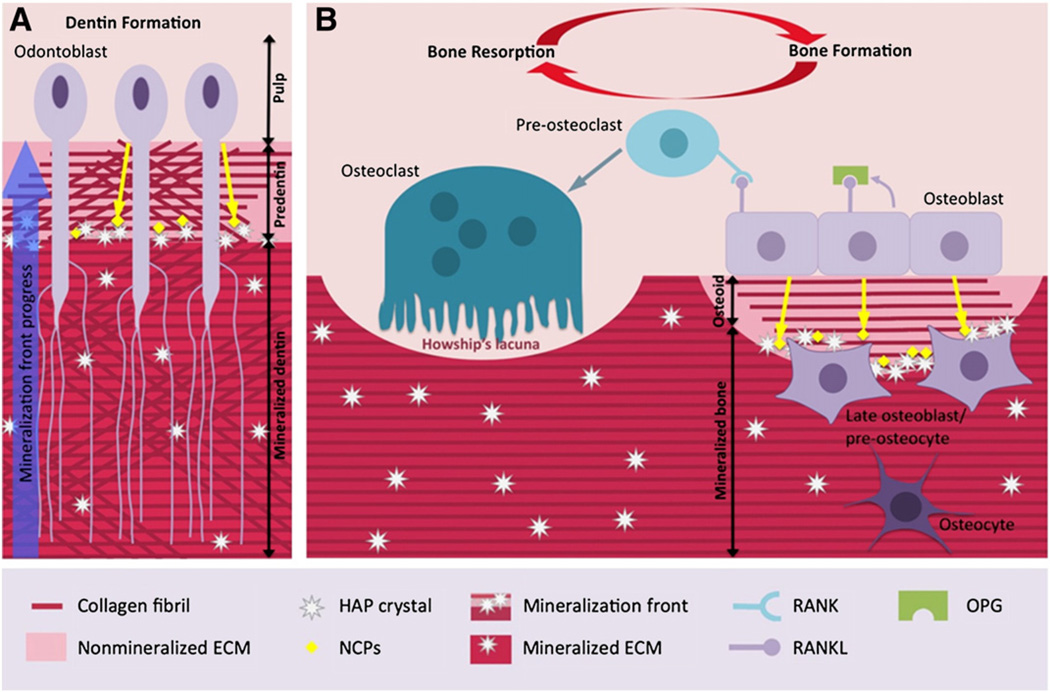
Fig. 1.
Characteristics of dentin formation and bone remodelling. A: Odontoblasts secrete an ECM composed of type I collagen and NCPs. Within the predentin, type I collagen molecules are assembled as fibrils. Mineralization occurs at the mineralization front by growth and fusion of calcospherites formed by hydroxyapatite (HAP) crystals. This mineralization process is controlled by NCPs and by mineral ion availability. Cell processes remain entrapped within dentin whereas cell bodies remain at the periphery of the pulp. B: Healthy bone is in a dynamic state: the activities of osteoblasts (bone formation) and osteoclasts (bone resorption) are regulated by the OPG/RANK/RANKL axis. RANKL stimulates bone resorption by increasing osteoclast differentiation whereas OPG, a soluble decoy receptor for RANKL, blocks osteoclast formation by inhibiting RANKL binding to RANK.