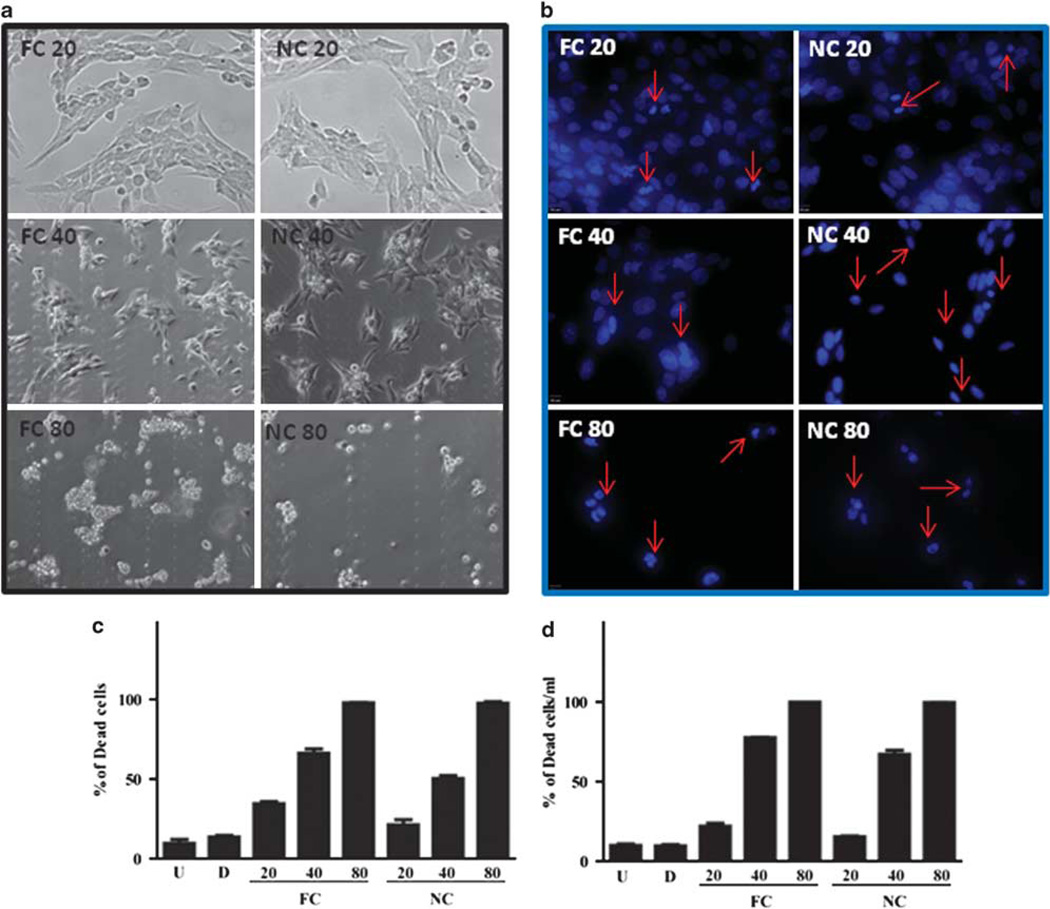
Figure 6.
In vitro NanoCurc™ treatment induces stellate cell apoptosis. Immortalized rat stellate cells, hepatic stellate cell line (HSC-T6), were plated and treated with the indicated doses of free curcumin (FC) dissolved in 0.1% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) or an equivalent dose of NanoCurc™ (NC) in plating media. Stellate cells were treated with 20, 40 and 80 µM of FC or NC. After treatment, cells were fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde, stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) and examined under ultraviolet (UV) light for morphological nuclear changes of apoptosis. Representative fluorescent photomicrographs show a dose-dependent increase in condensed apoptotic nuclei (red arrows) with nearly all apoptotic nuclei at the highest dose (80 µM). (a) Representative phase-contrast micrographs show shrinkage and condensation of the cells. (b, c) HSC-T6 were plated and treated with the indicated doses of FC, an equivalent dose of NC or 0.1% DMSO (d) and untreated (U). Stellate cells were treated with 20, 40 and 80 µM of FC or NC. After treatment, cells were fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde, and stained with DAPI. In all, 200 DAPI-positive cells were counted for live and dead cells. The percentage of the dead cells to the total cells was calculated as the total number of cells divided by the number of dead cell multiplied by 100. (d) HSC-T6 were plated and treated with the indicated doses of FC, an equivalent dose of NanoCurc™ (NC), 0.1% DMSO (d) and untreated (U). Stellate cells were treated with 20, 40 and 80 µM of FC or NanoCurc™. After treatment, the cells were trypsinized without ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) combined with an equal volume of Trypan blue and counted on hemocytometer for live and dead cells per ml. Percentage of dead cells were calculated by dividing Trypan-positive cells by the total number of cells multiplied by 100. All experiments are representative from two experiments.