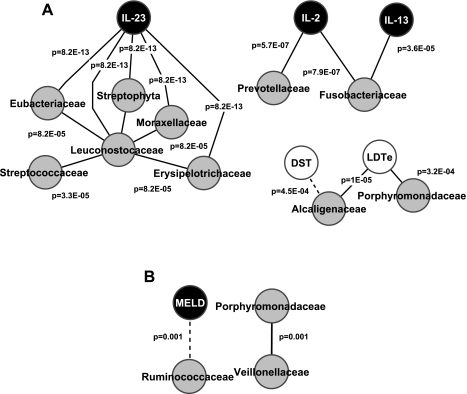
Fig. 2.
Correlation-network analysis of cirrhotic patients with and without hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Only correlations with a coefficient >r = 0.90 are displayed. Gray nodes indicate microbiome families; white nodes indicate cognitive tests; and black nodes are serum inflammatory markers. A black line connecting nodes indicates positive correlation, and a dashed line indicates negative correlation >0.90. The P values for the correlations are displayed on the lines connecting the nodes in A and B. MELD, model for end-stage liver disease score; DST, digit symbol test; LDTe, line drawing test errors. A: patients with HE (n = 17) have a high number of significant correlations. There are significant positive correlations between IL-23 and several bacterial families. Prevotellaceae and Fusobacteriaceae are positively correlated with inflammation. Because a low score on DST and high one on LDTe indicate poor performance, Alcaligenaceae and Porphyromonadaceae were correlated with poor cognition. The P values for all these correlations are less than the 4th decimal place, indicating a very high significance. B: patients without HE have very few significant correlations (n = 8). There was a significant negative correlation between MELD score and Ruminococcaceae and a positive correlation between Veillonellaceae and Porphyromonadaceae.